HIM-8 binds to the X chromosome pairing center and mediates chromosome-specific meiotic synapsis
- PMID: 16360035
- PMCID: PMC4435792
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.035
HIM-8 binds to the X chromosome pairing center and mediates chromosome-specific meiotic synapsis
Abstract
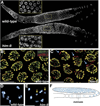
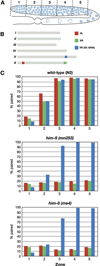
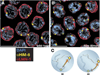
The him-8 gene is essential for proper meiotic segregation of the X chromosomes in C. elegans. Here we show that loss of him-8 function causes profound X chromosome-specific defects in homolog pairing and synapsis. him-8 encodes a C2H2 zinc-finger protein that is expressed during meiosis and concentrates at a site on the X chromosome known as the meiotic pairing center (PC). A role for HIM-8 in PC function is supported by genetic interactions between PC lesions and him-8 mutations. HIM-8 bound chromosome sites associate with the nuclear envelope (NE) throughout meiotic prophase. Surprisingly, a point mutation in him-8 that retains both chromosome binding and NE localization fails to stabilize pairing or promote synapsis. These observations indicate that stabilization of homolog pairing is an active process in which the tethering of chromosome sites to the NE may be necessary but is not sufficient.
Figures



Comment in
-
When size does not matter: pairing sites during meiosis.Cell. 2005 Dec 16;123(6):989-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.11.031. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16360029 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alpi A, Pasierbek P, Gartner A, Loidl J. Genetic and cytological characterization of the recombination protein RAD-51 in Caenorhabditis elegans . Chromosoma. 2003;112:6–16. - PubMed
-
- Anuradha S, Muniyappa K. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hop1 zinc finger motif is the minimal region required for its function in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2004b;279:28961–28969. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla N, Dernburg AF. A conserved checkpoint monitors meiotic chromosome synapsis in Caenorhabditis elegans . Science. 2005;310 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

