The pharmacognosy of Humulus lupulus L. (hops) with an emphasis on estrogenic properties
- PMID: 16360942
- PMCID: PMC1852439
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2004.07.006
The pharmacognosy of Humulus lupulus L. (hops) with an emphasis on estrogenic properties
Abstract
As the population ages, there is an ever-increasing need for therapeutic agents that can be used safely and efficaciously to manage symptoms related to postmenopausal estrogen deficiency. Endogenous estrogens, e.g., 17beta-estradiol, of exogenous mammalian origin, e.g., horses, have long been used to manage such symptoms. There are more than 20 different classes of phytochemicals that have demonstrated affinity for human estrogen receptors in vitro. Some studies on exogenous estrogenic substances of botanical origin (phytoestrogens), such as standardized formulations of plant extracts with in vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity from soy (Glycine max Merill.) and red clover (Trifolium pratense L.), suggest clinical efficacy. Few clinical data for phytoestrogens other than isoflavonoids are available. In an exhaustive review of the literature through 2003, only two clinical trials were identified that were designed to evaluate the effect of hops (Humulus lupulus L.) on symptoms related to menopause. Folkloric, chemical, and biological literature relating primarily to the use of hops for their estrogenic activity, and two human clinical trials, are reviewed.
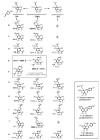
Figures
References
-
- Anonymous U.S. National Formulary of Unofficial Drugs: American Pharmaceutical Association. Mack Printing Co.; Easton, PA: 1946.
-
- Anonymous Rote Liste: Cantor GmbH. Satz-Rechen-Zentrum Hartmann & Heinemann; Berlin: 1985.
-
- Anonymous The Plant Names Project. International Plant Names Index. Published on the Internet. 1999. [Accessed October, 2003.]. http://www.ipni.org.
-
- Anonymous European Pharmacopoeia. 4th ed. Council of Europe; Strasbourg: 2002.
-
- Anonymous Beilstein Database (Beilstein-Institut zur Förderung der Chemischen Wissenschaften) 2003. [Accessed through November, 2003].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

