A novel integrin alpha5beta1 binding domain in module 4 of connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) promotes adhesion and migration of activated pancreatic stellate cells
- PMID: 16361307
- PMCID: PMC1856205
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2005.079178
A novel integrin alpha5beta1 binding domain in module 4 of connective tissue growth factor (CCN2/CTGF) promotes adhesion and migration of activated pancreatic stellate cells
Abstract
Background: Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) is upregulated in pancreatic fibrosis and desmoplastic pancreatic tumours. CCN2 interacts with integrin alpha5beta1 on pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) in which it stimulates fibrogenesis, adhesion, migration, and proliferation.
Aim: To determine the structural domain(s) in CCN2 that interact with integrin alpha5beta1 to regulation PSC functions.
Methods: Primary activated rat PSC were tested for their adherence to isoforms of CCN2 comprising modules 1-4 (CCN2(1-4)), modules 3-4 (CCN2(3-4)), module 3 alone (CCN2(3)), or module 4 alone (CCN2(4)). Adhesion studies were performed in the presence of EDTA, divalent cations, anti-integrin alpha5beta1 antibodies, CCN2 synthetic peptides, or heparin, or after pretreatment of the cells with heparinase, chondroitinase, or sodium chlorate. CCN2 integrin alpha5beta1 binding was analysed in cell free systems. The ability of CCN2(1-4), CCN2(3-4), or CCN2(4) to stimulate PSC migration was evaluated in the presence of anti-integrin alpha5beta1 or heparin.
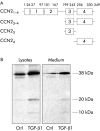
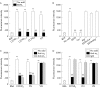
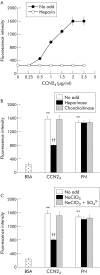
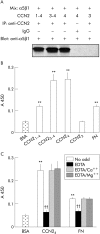
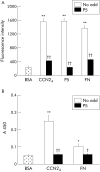
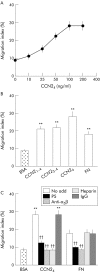
Results: PSC adhesion was stimulated by CCN2(1-4), CCN2(3-4), or CCN2(4) and supported by Mg2+ but not Ca2+. CCN2(4) supported PSC adhesion or migration were blocked by anti-integrin alpha5beta1 antibodies or by treatment of cells with heparinase or sodium chlorate. A direct interaction between CCN2(4) and integrin alpha5beta1 was demonstrated in cell free assays. The sequence GVCTDGR in module 4 mediated the binding between CCN2(4) and integrin alpha5beta1 as well as CCN2(4) mediated PSC adhesion and migration.
Conclusions: A GVCTDGR sequence in module 4 of CCN2 is a novel integrin alpha5beta1 binding site that is essential for CCN2 stimulated functions in PSC and which represents a new therapeutic target in PSC mediated fibrogenesis.
Similar articles
-
Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) in rat pancreatic stellate cell function: integrin alpha5beta1 as a novel CCN2 receptor.Gastroenterology. 2005 Sep;129(3):1019-30. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.06.067. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 16143139
-
Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) induces adhesion of rat activated hepatic stellate cells by binding of its C-terminal domain to integrin alpha(v)beta(3) and heparan sulfate proteoglycan.J Biol Chem. 2004 Mar 5;279(10):8848-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M313204200. Epub 2003 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14684735
-
CCN2 promotes keratinocyte adhesion and migration via integrin α5β1.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Nov 15;319(19):2938-46. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.08.021. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23988606
-
CCN proteins: multifunctional signalling regulators.Lancet. 2004 Jan 3;363(9402):62-4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15172-0. Lancet. 2004. PMID: 14723997 Review.
-
Regulation and function of connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 in tissue repair, scarring and fibrosis.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008 Apr;19(2):133-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.01.002. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2008. PMID: 18358427 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of pancreatic function by connective tissue growth factor (CTGF, CCN2).Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013 Feb;24(1):59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Aug 10. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013. PMID: 22884427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connective tissue growth factor (CCN2) and microRNA-21 are components of a positive feedback loop in pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) during chronic pancreatitis and are exported in PSC-derived exosomes.J Cell Commun Signal. 2014 Jun;8(2):147-56. doi: 10.1007/s12079-014-0220-3. Epub 2014 Jan 26. J Cell Commun Signal. 2014. PMID: 24464300 Free PMC article.
-
Pancreatic stellate cells: Key players in pancreatic health and diseases (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jul;30(1):109. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13233. Epub 2024 May 2. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 38695254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connective tissue growth factor with a novel fibronectin binding site promotes cell adhesion and migration during rat oval cell activation.Hepatology. 2008 Mar;47(3):996-1004. doi: 10.1002/hep.22079. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18167060 Free PMC article.
-
Connective tissue growth factor(CCN2), a pathogenic factor in diabetic nephropathy. What does it do? How does it do it?J Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Jun;3(2):95-104. doi: 10.1007/s12079-009-0038-6. Epub 2009 Feb 14. J Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19214781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brigstock D R. The connective tissue growth factor/cysteine‐rich 61/nephroblastoma overexpressed (CCN) family. Endocr Rev 199920189–206. - PubMed
-
- Lau L F, Lam S C. The CCN family of angiogenic regulators: the integrin connection. Exp Cell Res 199924844–57. - PubMed
-
- Rachfal A W, Brigstock D R. Structural and functional properties of CCN proteins. Vitam Horm 20057069–103. - PubMed
-
- Saluja A K, Bhagat L. Pathophysiology of alcohol‐induced pancreatic injury. Pancreas 200327327–331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous