Mineralocorticoid receptors are indispensable for nongenomic modulation of hippocampal glutamate transmission by corticosterone
- PMID: 16361444
- PMCID: PMC1323174
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507572102
Mineralocorticoid receptors are indispensable for nongenomic modulation of hippocampal glutamate transmission by corticosterone
Abstract
The adrenal hormone corticosterone transcriptionally regulates responsive genes in the rodent hippocampus through nuclear mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors. Via this genomic pathway the hormone alters properties of hippocampal cells slowly and for a prolonged period. Here we report that corticosterone also rapidly and reversibly changes hippocampal signaling. Stress levels of the hormone enhance the frequency of miniature excitatory postsynaptic potentials in CA1 pyramidal neurons and reduce paired-pulse facilitation, pointing to a hormone-dependent enhancement of glutamate-release probability. The rapid effect by corticosterone is accomplished through a nongenomic pathway involving membrane-located receptors. Unexpectedly, the rapid effect critically depends on the classical mineralocorticoid receptor, as evidenced by the effectiveness of agonists, antagonists, and brain-specific inactivation of the mineralocorticoid but not the glucocorticoid receptor gene. Rapid actions by corticosterone would allow the brain to change its function within minutes after stress-induced elevations of corticosteroid levels, in addition to responding later through gene-mediated signaling pathways.
Figures

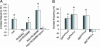
References
-
- Dallman, M. F., Akana, C. S., Cascio, D. N., Darlington, L. & Jacobson, N. (1987) Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 43, 113-173. - PubMed
-
- De Kloet, E. R., Joëls, M. & Holsboer, F. (2005) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 463-475. - PubMed
-
- Beato, M., Herrlich, P. & Schütz, G. (1995) Cell 83, 851-857. - PubMed
-
- Reichardt, H. M. & Schütz G. (1998) Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 146, 1-6. - PubMed
-
- Karst, H., Karten, Y. J., Reichardt, H. M., de Kloet, E. R., Schütz, G. & Joëls, M. (2000) Nat. Neurosci. 3, 977-978. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

