Raised CSF phospho-tau concentrations in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: diagnostic and pathological implications
- PMID: 16361602
- PMCID: PMC2117383
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2005.065755
Raised CSF phospho-tau concentrations in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: diagnostic and pathological implications
Abstract
Objective: To investigate whether phosphorylated tau protein (tau-pT181) is increased in variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and if the tau-pT181/tau protein ratio is useful for distinguishing between patients with and without CJD.
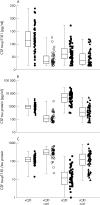
Methods: CSF tau protein and tau-pT181 were measured in 50 patients with sporadic CJD (sCJD), 51 patients with vCJD, 46 sCJD controls, and 37 vCJD controls, using Innotest hTau and Innotest P-Thr181, Innogenetics.
Results: Concentrations of CSF tau protein were increased in sCJD (5120 v 367 pg/ml in controls, p < 0.001) and vCJD (952 v 106 pg/ml, p < 0.001); tau-pT181 was also raised in sCJD (61 v 35 pg/ml in controls, p = 0.002) and vCJD (114 v 33 pg/ml, p < 0.001). Median concentrations of tau-pT181 were higher in vCJD than in sCJD (p < 0.001). The tau-pT181/tau protein ratio was lower than in controls in both sCJD (12 v 128 (p < 0.001)) and vCJD (119 v 279 (p < 0.001)). Mean tau-pT181/tau protein ratio was 10-fold higher in vCJD than in sCJD. Raised CSF tau protein had the highest efficiency for distinguishing sCJD and vCJD from controls.
Conclusions: CSF tau-pT181 concentrations are raised in vCJD and are higher than in sCJD. Measurement of CSF tau-pT181/tau protein ratio does not improve the diagnostic efficiency of CSF tau protein alone for either vCJD or sCJD. The higher concentration of CSF tau-pT181 found in vCJD suggests that unexplained pathogenic factors influence the phosphorylation of tau protein in vCJD patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
References
-
- Goedart M, Crowther R A, Garner C C. Molecular characterisation of microtubule‐associated proteins tau and MAP2. Trends Neurosci 199114193–199. - PubMed
-
- Otto M, Wiltfang J, Tumani H.et al Elevated levels of tau‐protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease. Neurosci Lett 1997225210–212. - PubMed
-
- Riemenschneider M, Wagenpfeil S, Vanderstichele H.et al Phospho‐tau/total tau ratio in cerebrospinal fluid discriminates Creutzfeldt‐Jakob disease from other dementias. Mol Psychiatry 20038343–347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical