Molecular basis of RNA recognition by the human alternative splicing factor Fox-1
- PMID: 16362037
- PMCID: PMC1356361
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600918
Molecular basis of RNA recognition by the human alternative splicing factor Fox-1
Abstract
The Fox-1 protein regulates alternative splicing of tissue-specific exons by binding to GCAUG elements. Here, we report the solution structure of the Fox-1 RNA binding domain (RBD) in complex with UGCAUGU. The last three nucleotides, UGU, are recognized in a canonical way by the four-stranded beta-sheet of the RBD. In contrast, the first four nucleotides, UGCA, are bound by two loops of the protein in an unprecedented manner. Nucleotides U1, G2, and C3 are wrapped around a single phenylalanine, while G2 and A4 form a base-pair. This novel RNA binding site is independent from the beta-sheet binding interface. Surface plasmon resonance analyses were used to quantify the energetic contributions of electrostatic and hydrogen bond interactions to complex formation and support our structural findings. These results demonstrate the unusual molecular mechanism of sequence-specific RNA recognition by Fox-1, which is exceptional in its high affinity for a defined but short sequence element.
Figures
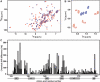
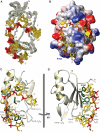
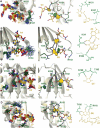


References
-
- Baur M, Gemmecker G, Kessler H (1998) C-13-NOESY-HSQC with split carbon evolution for increased resolution with uniformly labeled proteins. J Magn Reson 132: 191–196 - PubMed
-
- Bax A, Clore G, Gronenborn A (1990) H-1-H-1 correlation via isotropic mixing of C-13 magentization, a new 3-domensional approach for assigning H-1 and C-13 spectra of C-13 enriched peoteins. J Magn Reson 88: 425–431
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

