A 'Collagen Hug' model for Staphylococcus aureus CNA binding to collagen
- PMID: 16362049
- PMCID: PMC1356329
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600888
A 'Collagen Hug' model for Staphylococcus aureus CNA binding to collagen
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2006 Feb 22;25(4):921
Abstract
The structural basis for the association of eukaryotic and prokaryotic protein receptors and their triple-helical collagen ligand remains poorly understood. Here, we present the crystal structures of a high affinity subsegment of the Staphylococcus aureus collagen-binding CNA as an apo-protein and in complex with a synthetic collagen-like triple helical peptide. The apo-protein structure is composed of two subdomains (N1 and N2), each adopting a variant IgG-fold, and a long linker that connects N1 and N2. The structure is stabilized by hydrophobic inter-domain interactions and by the N2 C-terminal extension that complements a beta-sheet on N1. In the ligand complex, the collagen-like peptide penetrates through a spherical hole formed by the two subdomains and the N1-N2 linker. Based on these two structures we propose a dynamic, multistep binding model, called the 'Collagen Hug' that is uniquely designed to allow multidomain collagen binding proteins to bind their extended rope-like ligand.
Figures

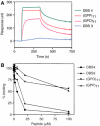

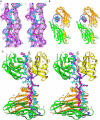



References
-
- Bella J, Eaton M, Brodsky B, Berman HM (1994) Crystal and molecular structure of a collagen-like peptide at 1.9 Å resolution [see comment]. Science 266: 75–81 - PubMed
-
- Brodsky B, Persikov AV (2005) Molecular structure of the collagen triple helix. Adv Protein Chem 70: 301–339 - PubMed
-
- Brunger AT, Adams PD, Clore GM, DeLano WL, Gros P, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Jiang JS, Kuszewski J, Nilges M, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Rice LM, Simonson T, Warren G (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 54 (Part 5): 905–921 - PubMed
-
- Carson M (1997) Ribbons. Methods Enzymol 277: 493–505 - PubMed
-
- Clemetson KJ, Clemetson JM (2001) Platelet collagen receptors. Thromb Haemost 86: 189–197 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

