Total hip arthroplasty for developmental hip dysplasia
- PMID: 16362384
- PMCID: PMC2254666
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-005-0027-1
Total hip arthroplasty for developmental hip dysplasia
Abstract
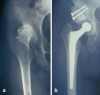
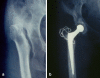
We reviewed 38 hip replacements in 33 female patients (mean age 55.3 years) with developmental hip dysplasia. One patient had died and the remaining 32 patients (36 hips) had a mean follow-up of 12.2 years (range 8-19 years). All hips were replaced using the Müller cemented implant, and in 32 hips bulk femoral head autograft was used. In 33 hips the socket was reconstructed at the level of the true acetabulum. Complications included one intra-operative femoral fracture and two early dislocations. Correction of leg length discrepancy was possible in 30 patients. The post-operative mean modified Merle d'Aubigne and Postel scores for pain, movement and walking were 5.9, 5, and 5.3 respectively. One cup was revised due to aseptic loosening at ten years. All grafts united, but minor graft resorption was noticed in 24 hips, moderate in 2 hips and major in 1 hip.
Nous avons examiné 38 remplacements prothétiques de la hanche chez 33 femmes (âge moyen 55,3 ans) avec une dysplasie de la hanche. Une patiente était décédée et les 32 autres (36 hanches) avaient un suivi moyen de 12,2 ans ( 8 à 19). Toutes les hanches ont eu un implant type Müller cimenté et pour 32 une autogreffe massive de tête fémorale a été utilisé. Pour 33 hanches la cavité a été reconstruite au niveau du paléo-cotyle. Les complications comprenaient une fracture fémorale opératoire et deux luxations précoces. La correction de l’inégalité de longueur des membres inférieurs était obtenue chez 30 malades. Le score postopératoire modifié de Merle d’Aubigné et Postel pour la douleur, la mobilité et la marche étaient en moyenne de 5,9, 5 et 5,3 respectivement. Une cupule a été révisée pour un descellement aseptique à 10 ans. Toutes les greffes ont consolidé, mais une résorption mineure de la greffe a été remarquée dans 24 hanches, une résorption modéré dans deux hanches et majeure dans une.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Cemented total hip arthroplasty for severe dysplasia or congenital dislocation of the hip].Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2002;36(3):195-202. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2002. PMID: 12510076 Turkish.
-
Cemented total hip arthroplasty with autogenous acetabular bone grafting for hips with developmental dysplasia in adults: the results at a minimum of ten years.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000 Apr;82(3):375-7. doi: 10.1302/0301-620x.82b3.10465. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2000. PMID: 10813172
-
[Total hip arthroplasty with uncemented cup and femoral head autografts for coxarthrosis due to dysplasia].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004 Aug 22;42(16):1006-9. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15363240 Chinese.
-
Total hip replacement for the dislocated hip.Instr Course Lect. 2001;50:307-16. Instr Course Lect. 2001. PMID: 11372330 Review.
-
Total hip arthroplasty for adult hip dysplasia.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012 Oct 3;94(19):1809-21. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.K.00779. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012. PMID: 23032592 Review.
Cited by
-
Total Hip Replacement in Developmental Hip Dysplasia: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2021 Apr 29;13(4):e14763. doi: 10.7759/cureus.14763. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34094728 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical treatment for young adult hip dysplasia: joint-preserving options.Int Orthop. 2016 May;40(5):891-900. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2927-z. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Int Orthop. 2016. PMID: 26216530 Review.
-
Mid-term results of short-stem total hip arthroplasty in patients with Crowe type I and II developmental dysplasia of the hip.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021 Feb;31(2):319-325. doi: 10.1007/s00590-020-02777-1. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2021. PMID: 32875473
-
Mid-term low back pain improvement after total hip arthroplasty in 306 patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Mar 17;18(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03701-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 36932447 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of mid-term outcomes in 334 developmental dysplasia hips treated with total hip arthroplasty.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Aug 7;26(1):762. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-09041-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40775631 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '10199272', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10199272/'}]}
- Anderson MJ, Harris WH (1999) Total hip arthroplasty with insertion of the acetabular component without cement in hips with total congenital dislocation or marked congenital dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81:347–354 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '3819398', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3819398/'}]}
- Aronson J (1986) Osteoarthritis of the young adult hip: etiology and treatment. Instr Course Lect 35:119–128 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '4217797', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4217797/'}]}
- Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH Jr (1973) Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55:1629–1632 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0883-5403(96)80113-6', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0883-5403(96)80113-6'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8872579', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8872579/'}]}
- Cameron HU, Botsford DJ, Park YS (1996) Influence of the Crowe rating on the outcome of total hip arthroplasty in congenital hip dysplasia. J Arthroplasty 11:582–587 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '365863', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/365863/'}]}
- Crowe JF, Mani VJ, Ranawat CS (1979) Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:15–23 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

