Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells
- PMID: 16365161
- PMCID: PMC2171318
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200510043
Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells
Abstract
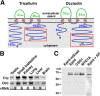
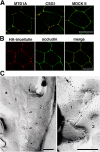
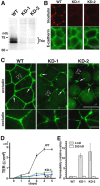
For epithelia to function as barriers, the intercellular space must be sealed. Sealing two adjacent cells at bicellular tight junctions (bTJs) is well described with the discovery of the claudins. Yet, there are still barrier weak points at tricellular contacts, where three cells join together. In this study, we identify tricellulin, the first integral membrane protein that is concentrated at the vertically oriented TJ strands of tricellular contacts. When tricellulin expression was suppressed with RNA interference, the epithelial barrier was compromised, and tricellular contacts and bTJs were disorganized. These findings indicate the critical function of tricellulin for formation of the epithelial barrier.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson, J.M., C.M. Van Itallie, and A.S. Fanning. 2004. Setting up a selective barrier at the apical junction complex. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 16:140–145. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp, T.R., R. Bernards, and R. Agami. 2002. A system for stable expression of short interfering RNAs in mammalian cells. Science. 296:550–553. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

