Class II-restricted T cell receptor engineered in vitro for higher affinity retains peptide specificity and function
- PMID: 16365315
- PMCID: PMC1323173
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507554102
Class II-restricted T cell receptor engineered in vitro for higher affinity retains peptide specificity and function
Abstract
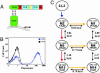
The T cell receptor (TCR) alphabeta heterodimer determines the peptide and MHC specificity of a T cell. It has been proposed that in vivo selection processes maintain low TCR affinities because T cells with higher-affinity TCRs would (i) have reduced functional capacity or (ii) cross-react with self-peptides resulting in clonal deletion. We used the class II-restricted T cell clone 3.L2, specific for murine hemoglobin (Hb/I-E(k)), to explore these possibilities by engineering higher-affinity TCR mutants. A 3.L2 single-chain TCR (Vbeta-linker-Valpha) was mutagenized and selected for thermal stability and surface expression in a yeast display system. Stabilized mutants were used to generate a library with CDR3 mutations that were selected with Hb/I-E(k) to isolate a panel of affinity mutants with K(D) values as low as 25 nM. Kinetic analysis of soluble single-chain TCRs showed that increased affinities were the result of both faster on-rates and slower off-rates. T cells transfected with the mutant TCRs and wild-type TCR responded to similar concentrations of peptide, indicating that the increased affinity was not detrimental to T cell activation. T cell transfectants maintained exquisite hemoglobin peptide specificity, but an altered peptide ligand that acted as an antagonist for the wild-type TCR was converted to a strong agonist with higher-affinity TCRs. These results show that T cells with high-affinity class II reactive TCRs are functional, but there is an affinity threshold above which an increase in affinity does not result in significant enhancement of T cell activation.
Figures

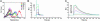

References
-
- Starr, T. K., Jameson, S. C. & Hogquist, K. A. (2003) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 139-176. - PubMed
-
- Davis, M. M., Boniface, J. J., Reich, Z., Lyons, D., Hampl, J., Arden, B. & Chien, Y. (1998) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 523-544. - PubMed
-
- Gascoigne, N. R. J., Zai, T. & Alam, S. M. (2001) Exp. Rev. Mol. Med., http://www-ermm.cbcu.cam.ac.uk/01002502h.htm. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

