P2Y2 receptor activates nerve growth factor/TrkA signaling to enhance neuronal differentiation
- PMID: 16365320
- PMCID: PMC1323158
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505913102
P2Y2 receptor activates nerve growth factor/TrkA signaling to enhance neuronal differentiation
Abstract
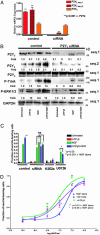
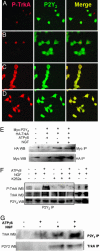
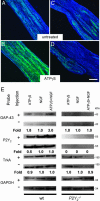
Neurotrophins are essential for neuronal differentiation, but the onset and the intensity of neurotrophin signaling within the neuronal microenvironment are poorly understood. We tested the hypothesis that extracellular nucleotides and their cognate receptors regulate neurotrophin-mediated differentiation. We found that 5'-O-(3-thio)triphosphate (ATPgammaS) activation of the G protein-coupled receptor P2Y(2) in the presence of nerve growth factor leads to the colocalization and association of tyrosine receptor kinase A and P2Y(2) receptors and is required for enhanced neuronal differentiation. Consistent with these effects, ATPgammaS promotes phosphorylation of tyrosine receptor kinase A, early response kinase 1/2, and p38, thereby enhancing sensitivity to nerve growth factor and accelerating neurite formation in both PC12 cells and dorsal root ganglion neurons. Genetic or small interfering RNA depletion of P2Y(2) receptors abolished the ATPgammaS-mediated increase in neuronal differentiation. Moreover, in vivo injection of ATPgammaS into the sciatic nerve increased growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43), a marker for axonal growth, in wild-type but not P2Y(2)(-/-) mice. The interactions of tyrosine kinase- and P2Y(2)-signaling pathways provide a paradigm for the regulation of neuronal differentiation and suggest a role for P2Y(2) as a morphogen receptor that potentiates neurotrophin signaling in neuronal development and regeneration.
Figures
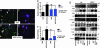

References
-
- Yamamoto, N., Tamada, A. & Murakami, F. (2002) Prog. Neurobiol. 68, 393-407. - PubMed
-
- Boglari, G. & Szeberenyi, J. (2001) Eur. J. Neurosci. 14, 1445-1454. - PubMed
-
- Gavazzi, I. & Cowen, T. (1996) J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 58, 1-10. - PubMed
-
- Chuang, H. H., Prescott, E. D., Kong, H., Shields, S., Jordt, S. E., Basbaum, A. I., Chao, M. V. & Julius, D. (2001) Nature 411, 957-962. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- GM66232/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RR04050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- GM007240/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA007315/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- NS052189/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007315/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007240/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL58120/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR004050/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- DA07315-03/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS052189/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS051470/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM066232/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- NS051470/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL058120/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

