Randomized study of combined universal family and school preventive interventions: patterns of long-term effects on initiation, regular use, and weekly drunkenness
- PMID: 16366809
- PMCID: PMC2409287
- DOI: 10.1037/0893-164X.19.4.372
Randomized study of combined universal family and school preventive interventions: patterns of long-term effects on initiation, regular use, and weekly drunkenness
Abstract
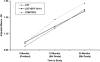
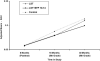
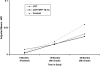
This study reports findings on a combined family and school-based competency-training intervention from an in-school assessment 2.5 years past baseline, as a follow-up to an earlier study of substance initiation. Increased rates of observed alcohol use and an additional wave of data allowed evaluation of regular alcohol use and weekly drunkenness, with both point-in-time and growth curve analyses. Thirty-six rural schools were randomly assigned to (a) a combined family and school intervention condition, (b) a school-only condition, or (c) a control condition. The earlier significant outcome on a substance initiation index was replicated, and positive point-in-time results for weekly drunkenness were observed, but there were no statistically significant outcomes for regular alcohol use. Discussion focuses on factors relevant to the mix of significant longitudinal results within a consistent general pattern of positive intervention-control differences.
((c) 2005 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
Comment in
-
Family-Based Interventions in Preventing Children and Adolescents from Using Tobacco: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Acad Pediatr. 2016 Jul;16(5):419-429. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2015.12.006. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Acad Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26892909 Review.
References
-
- Ackerman S, Zuroff DC, Moskowitz DS. Generativity in midlife and young adults: Links to agency, communion, and subjective well-being. International Journal of Aging and Human Development. 2000;50:17–41. - PubMed
-
- Anthony J. Selected issued pertinent to epidemiology of adolescent drug use and dependence; Paper presented at the meeting of the Annenberg Commission on Adolescent Substance Abuse; Philadelphia. Aug, 2003.
-
- Azevedo K, Redmond C, Lillehoj C, Spoth RL. Contradictions across in-school and in-home reports of adolescent substance use initiation; Poster presented at the meeting of the Society for Prevention Research; Washington, DC. Jun, 2003.
-
- Bailey SL. The measurement of problem drinking in young adulthood. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1999;60:234–244. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Social learning theory. Prentice Hall; Englewood Cliffs, NJ: 1977.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

