NG2: a component of the glial scar that inhibits axon growth
- PMID: 16367799
- PMCID: PMC1571583
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00452.x
NG2: a component of the glial scar that inhibits axon growth
Abstract
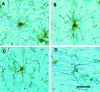
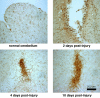
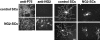
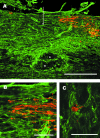
NG2 is a high-molecular-weight chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan found on the surfaces of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPCs). Here we review the history and biology of OPCs with an emphasis on their functions after experimentally induced CNS injury. Injury to brain or spinal cord results in the rapid accumulation of NG2-expressing OPCs in the glial scar that forms at the injury site. The glial scar is considered a biochemical and physical barrier to successful axon regeneration and the functional properties of NG2 suggest that it, along with other macromolecules, participates in the creation of this growth-inhibitory environment. NG2 is an important target for therapies designed to promote successful axon regrowth.
Figures
References
-
- Bradbury EJ, Moon LD, Popat RJ, et al. Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature. 2002;416:636–640. - PubMed
-
- Bu J, Akhtar N, Nishiyama A. Transient expression of the NG2 proteoglycan by a sub-population of activated macrophages in an excitotoxic hippocampal lesion. Glia. 2001;34:296–310. - PubMed
-
- Butt AM, Duncan A, Hornby MF, et al. Cells expressing the NG2 antigen contact nodes of Ranvier in adult CNS white matter. Glia. 1999;26:84–91. - PubMed
-
- Butt AM, Kiff J, Hubbard P, Berry M. Synaptocyte: new functions for novel NG2 expressing glia. J Neurocytol. 2002;31:551–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

