Atypical development of Sertoli cells and impairment of spermatogenesis in the hypogonadal (hpg) mouse
- PMID: 16367806
- PMCID: PMC1571580
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2005.00493.x
Atypical development of Sertoli cells and impairment of spermatogenesis in the hypogonadal (hpg) mouse
Abstract
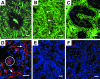
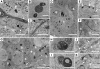
Testes of hypogonadal (hpg) mice show arrested postnatal development due to congenital deficiencies of gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and gonadotrophin synthesis and secretion. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), androgen or oestrogen treatment restore qualitatively normal spermatogenesis in hpg testes. Understanding the cellular and molecular changes accompanying hormone-induced spermatogenesis in hpg mice requires detailed morphological analyses of the germ cells and Sertoli cells in the untreated hpg testis. We compared seminiferous epithelial cytology in adult hpg, immature and adult wild-type mice using unbiased optical disector-based stereology, immunolocalization of Sertoli cell microtubules (MT), espin (a component of the blood-testis barrier), markers of Sertoli cell maturity (p27(kip1) and WT-1), and electron microscopy. Hpg testes had marked reductions in weight, seminiferous cord volume and length, and severe spermatogenic impairment with germ cells per testis < 1% of adult wild-type testes. Sertoli cell nuclei expressed WT-1 in hpg testes, but often were centrally located, similar to 9-14-day-old wild-type testes, and they expressed p27(kip1), indicating that hpg Sertoli cells were post-mitotic. Hpg testes had significantly (P < 0.05) reduced Sertoli cells per testis (0.56 million) compared with 10-day wild-type (1.15 million) and adult wild-type testes (2.06 million). Immunofluorescence labelling of normal adult Sertoli cells showed supranuclear MT columns and basally located espin, but these features were absent in 10-day-old and hpg Sertoli cells. Hpg Sertoli cells showed pleomorphic nuclear ultrastructure with mature-type nucleoli, similar to normal adult-type Sertoli cells, but hpg Sertoli cells exhibited incomplete tight junctions that lacked ectoplasmic specializations. We conclude that in hpg mice, chronic gonadotrophin insufficiency restrains Sertoli cell proliferation and maturation, forming pseudo-adult-type Sertoli cells that are incapable of supporting germ cell proliferation and maturation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Androgen initiates Sertoli cell tight junction formation in the hypogonadal (hpg) mouse.Biol Reprod. 2012 Aug 23;87(2):38. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.094318. Print 2012 Aug. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22623623
-
Complete Sertoli cell proliferation induced by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) independently of luteinizing hormone activity: evidence from genetic models of isolated FSH action.Endocrinology. 2004 Apr;145(4):1587-93. doi: 10.1210/en.2003-1164. Epub 2004 Jan 15. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 14726449
-
Sertoli and germ cell development in hypogonadal (hpg) mice expressing transgenic follicle-stimulating hormone alone or in combination with testosterone.Endocrinology. 2003 Feb;144(2):509-17. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220710. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12538611
-
The hypogonadal (hpg) mouse as a model to investigate the estrogenic regulation of spermatogenesis.Hum Fertil (Camb). 2006 Sep;9(3):127-35. doi: 10.1080/14647270500509103. Hum Fertil (Camb). 2006. PMID: 17008264 Review.
-
Biology of the Sertoli Cell in the Fetal, Pubertal, and Adult Mammalian Testis.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2016;58:225-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-31973-5_9. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2016. PMID: 27300181 Review.
Cited by
-
The mouse cytosine-5 RNA methyltransferase NSun2 is a component of the chromatoid body and required for testis differentiation.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;33(8):1561-70. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01523-12. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23401851 Free PMC article.
-
Nesprin-3 connects plectin and vimentin to the nuclear envelope of Sertoli cells but is not required for Sertoli cell function in spermatogenesis.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Aug;24(15):2454-66. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-02-0100. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23761073 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of FSH on testicular morphology and spermatogenesis in gonadotrophin-deficient hypogonadal mice lacking androgen receptors.Reproduction. 2010 Jan;139(1):177-84. doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0377. Reproduction. 2010. PMID: 19846485 Free PMC article.
-
A Wt1-Dmrt1 transgene restores DMRT1 to sertoli cells of Dmrt1(-/-) testes: a novel model of DMRT1-deficient germ cells.Biol Reprod. 2013 Feb 1;88(2):51. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.103135. Print 2013 Feb. Biol Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23255335 Free PMC article.
-
The interconnection between cytokeratin and cell membrane-bound β-catenin in Sertoli cells derived from juvenile Xenopus tropicalis testes.Biol Open. 2019 Dec 20;8(12):bio043950. doi: 10.1242/bio.043950. Biol Open. 2019. PMID: 31822471 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan CM, Haywood M, Swaraj S, et al. A novel transgenic model to characterize the specific effects of follicle-stimulating hormone on gonadal physiology in the absence of luteinizing hormone actions. Endocrinology. 2001;142:2213–2220. - PubMed
-
- Allan CM, Garcia A, Spaliviero J, et al. Complete Sertoli cell proliferation induced by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) independently of luteinizing hormone activity: evidence from genetic models of isolated FSH action. Endocrinology. 2004;145:1587–1593. - PubMed
-
- Baker PJ, O'Shaughnessy PJ. Role of gonadotrophins in regulating numbers of Leydig and Sertoli cells during fetal and postnatal development in mice. Reproduction. 2001;122:227–234. - PubMed
-
- Bartles JR, Wierda A, Zheng L. Identification and characterization of espin, an actin-binding protein localized to the F-actin-rich junctional plaques of Sertoli cell ectoplasmic specializations. J Cell Sci. 1996;109:1229–1239. - PubMed
-
- Bendsen E, Byskov AG, Laursen SB, Larsen HP, Andersen CY, Westergaard LG. Number of germ cells and somatic cells in human fetal testes during the first weeks after sex differentiation. Hum Reprod. 2003;18:13–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

