Enhanced efficacy of radiation-induced gene therapy in mice bearing lung adenocarcinoma xenografts using hypoxia responsive elements
- PMID: 16367913
- PMCID: PMC11158909
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2005.00129.x
Enhanced efficacy of radiation-induced gene therapy in mice bearing lung adenocarcinoma xenografts using hypoxia responsive elements
Abstract
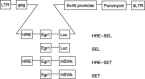
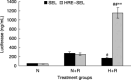
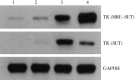
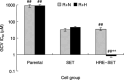
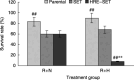
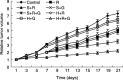
The aim of the present study was to investigate whether the hypoxia responsive element (HRE) could be used to enhance suicide gene (HSV-tk) expression and tumoricidal activity in radiation-controlled gene therapy of human lung adenocarcinoma xenografts. A chimeric promoter, HRE-Egr, was generated by directly linking a 0.3-kb fragment of HRE to a 0.6-kb human Egr-1 promoter. Retroviral vectors containing luciferase or the HSV-tk gene driven by Egr-1 or HRE-Egr were constructed. A human adenocarcinoma cell line (A549) was stably transfected with the above vectors using the lipofectamine method. The sensitivity of transfected cells to prodrug ganciclovir (GCV) and cell survival rates were analyzed after exposure to a dose of 2 Gy radiation and hypoxia (1%). In vivo, tumor xenografts in BALB/c mice were transfected with the constructed retroviruses and irradiated to a total dose of 6 Gy, followed by GCV treatment (20 mg/kg for 14 days). When the HSV-tk gene controlled by the HRE-Egr promoter was introduced into A549 cells by a retroviral vector, the exposure to 1% O(2) and 2 Gy radiation induced significant enhancement of GCV cytotoxicity to the cells. Moreover, in nude mice bearing solid tumor xenografts, only the tumors infected with the hybrid promoter-containing virus gradually disappeared after GCV administration and radiation. These results indicate that HRE can enhance transgene expression and tumoricidal activity in HSV-tk gene therapy controlled by ionizing radiation in hypoxic human lung adenocarcinoma.
(Cancer Sci 2005; 96: 918 - 924).
Figures
Similar articles
-
[HSV-TK gene therapy of lung adenocarcinoma xenografts using a hypoxia/radiation dual-sensitive promoter].Ai Zheng. 2004 Jul;23(7):788-93. Ai Zheng. 2004. PMID: 15248913 Chinese.
-
[Oncostatin M gene therapy in mice bearing lung adenocarcinoma xenograft using a hypoxia/radiation dual-sensitive promoter].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2004 Apr;27(4):240-3. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2004. PMID: 15144614 Chinese.
-
An autologous in situ tumor vaccination approach for hepatocellular carcinoma. 1. Flt3 ligand gene transfer increases antitumor effects of a radio-inducible suicide gene therapy in an ectopic tumor model.Radiat Res. 2014 Aug;182(2):191-200. doi: 10.1667/RR13594.1. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Radiat Res. 2014. PMID: 24972258
-
Gene therapy targeting for hepatocellular carcinoma: selective and enhanced suicide gene expression regulated by a hypoxia-inducible enhancer linked to a human alpha-fetoprotein promoter.Cancer Res. 2001 Apr 1;61(7):3016-21. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11306481
-
[Experimental study on lung carcinoma-targeted suicide gene therapy induced by irradiation].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2003 Feb;26(2):84-7. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 12783658 Chinese.
Cited by
-
MiRNA-Embedded ShRNAs for Radiation-Inducible LGMN Knockdown and the Antitumor Effects on Breast Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 22;11(9):e0163446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163446. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27656894 Free PMC article.
-
Radiation-induced SOD2 overexpression sensitizes colorectal cancer to radiation while protecting normal tissue.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7791-7800. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13954. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27999194 Free PMC article.
-
p53 activated by AND gate genetic circuit under radiation and hypoxia for targeted cancer gene therapy.Cancer Sci. 2015 Sep;106(9):1163-73. doi: 10.1111/cas.12739. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26177264 Free PMC article.
-
Optimized ultrasound-mediated gene transfection in cancer cells.Cancer Sci. 2006 Oct;97(10):1111-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00286.x. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Cancer Sci. 2006. PMID: 16925580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kufe D, Weichselbaum R. Radiation therapy: activation for gene transcription and the development of genetic radiotherapy‐therapeutic strategies in oncology. Cancer Biol Ther 2003; 2: 326–9. - PubMed
-
- Xia J, Xia K, Feng Y et al. The combination of suicide gene therapy and radiation enhances the killing of nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenographs. J Radiat Res (Tokyo) 2004; 45: 281–9. - PubMed
-
- Hsu H, Rainov NG, Quinones A et al. Combined radiation and cytochrome CYP4B1/4‐ipomeanol gene therapy using the EGR1 promoter. Anticancer Res 2003; 23: 2723–8. - PubMed
-
- Hallahan DE, Weichselbaum RR. Role of gene therapy in radiation oncology. Cancer Treat Res 1998; 93: 153–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

