Dose-dependent induction of IL-6 by plant-derived proteases in vitro
- PMID: 16367938
- PMCID: PMC1809566
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02970.x
Dose-dependent induction of IL-6 by plant-derived proteases in vitro
Abstract
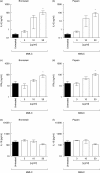
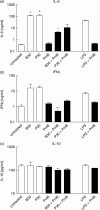
Oral administration of proteases such as bromelain and papain is commonly used in patients with a wide range of inflammatory conditions, but their molecular and cellular mechanisms of action are still poorly understood. The aim of our study was to investigate the impact of these proteases on the release of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and other cytokines in the recently described modified mixed lymphocyte culture (MMLC) test system which is based on the mutual interaction of cells of the innate and adaptive immunity. Bromelain and papain enhanced IL-6 production dose-dependently up to 400-fold in MMLC before and up to 30-fold after neutralization of LPS content of proteases using polymyxin B, indicating that IL-6 induction by protease treatment was attributable to both protease action and LPS content of enzyme preparations. The production of IFNgamma and IL-10 was not altered by bromelain or papain, indicating a selective and differential immune activation. Both proteases impaired cytokine stability, cell proliferation and expression of cell surface molecules like CD14 only marginally, suggesting no impact of these mechanisms on protease-mediated cytokine release. These findings might provide the mechanistic rationale for the current use of proteases in wound healing and tissue regeneration since these processes depend on IL-6 induction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial on the immunomodulating activities of low- and high-dose bromelain after oral administration - new evidence on the antiinflammatory mode of action of bromelain.Phytother Res. 2013 Feb;27(2):199-204. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4678. Epub 2012 Apr 20. Phytother Res. 2013. PMID: 22517542 Clinical Trial.
-
Bromelain inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine production in human THP-1 monocytes via the removal of CD14.Immunol Invest. 2008;37(4):263-77. doi: 10.1080/08820130802083622. Immunol Invest. 2008. PMID: 18569070
-
In vitro study on the immunological effect of bromelain and trypsin on mononuclear cells from humans.Eur J Med Res. 2005 Aug 17;10(8):325-31. Eur J Med Res. 2005. PMID: 16131473
-
Combined activation of innate and T cell immunity for recognizing immunomodulatory properties of therapeutic agents.J Leukoc Biol. 2004 Apr;75(4):624-30. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1003454. Epub 2004 Jan 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2004. PMID: 14704370
-
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein down-regulates the expression of interleukin-6 by human gingival fibroblast.J Periodontal Res. 2005 Oct;40(5):407-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.2005.00822.x. J Periodontal Res. 2005. PMID: 16105094
Cited by
-
Study of the Radiosensitizing and Radioprotective Efficacy of Bromelain (a Pineapple Extract): In Vitro and In Vivo.Integr Cancer Ther. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1534735420950468. doi: 10.1177/1534735420950468. Integr Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32783540 Free PMC article.
-
Bromelain down-regulates myofibroblast differentiation in an in vitro wound healing assay.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Oct;386(10):853-63. doi: 10.1007/s00210-013-0890-z. Epub 2013 Jun 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23771413
-
A Randomized Controlled Trial of the Efficacy of Systemic Enzymes and Probiotics in the Resolution of Post-COVID Fatigue.Medicines (Basel). 2021 Aug 30;8(9):47. doi: 10.3390/medicines8090047. Medicines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34564089 Free PMC article.
-
Bromelain treatment decreases secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by colon biopsies in vitro.Clin Immunol. 2008 Mar;126(3):345-52. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Dec 21. Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18160345 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing extraction efficiency of carpaine in Carica papaya L. leaves: coupling acid-base extraction with surfactant-assisted micro-flotation.RSC Adv. 2024 Sep 11;14(39):28768-28778. doi: 10.1039/d4ra05132g. eCollection 2024 Sep 4. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39263437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leipner J, Iten F, Saller R. Therapy with proteolytic enzymes in rheumatic disorders. Biodrugs. 2001;15:779–89. - PubMed
-
- Shahid SK, Turakhia NH, Kundra M, Shanbag P, Daftary GV, Schiess W. Efficacy and safety of phlogenzym – a protease formulation, in sepsis in children. J Assoc Physicians India. 2002;50:527–31. - PubMed
-
- Desser L, Rehberger A. Induction of tumor necrosis factor in human peripheral-blood mononuclear cells by proteolytic enzymes. Oncology. 1990;47:475–7. - PubMed
-
- Desser L, Rehberger A, Paukovits W. Proteolytic enzymes and amylase induce cytokine production in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro. Cancer Biother. 1994;9:253–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

