A form of circulating interleukin-6 receptor component soluble gp130 as a potential interleukin-6 inhibitor in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 16367943
- PMCID: PMC1809568
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02960.x
A form of circulating interleukin-6 receptor component soluble gp130 as a potential interleukin-6 inhibitor in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
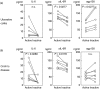
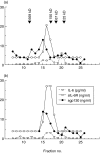
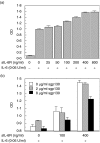
The presence and the role of soluble gp130, the soluble form of a component of the interleukin (IL)-6 receptor complex, were investigated in inflammatory bowel disease. The serum concentrations of soluble gp130 were increased in ulcerative colitis (active disease, median, 93.5 ng/ml; interquartile range, 26-125 ng/ml; inactive disease, 81 ng/ml, 24.8-137.3 ng/ml) and to a lesser extent in Crohn's disease (active disease, 66 ng/ml, 44.4-87.6 ng/ml; inactive disease, 63 ng/ml, 43.5-82.5 ng/ml) compared to normal controls (43 ng/ml, 27-59 ng/ml). Paired analysis of serum samples showed a decrease of IL-6 and soluble IL-6 receptor concentrations in both diseases and an increase of soluble gp130 concentrations, especially in ulcerative colitis, just after the resolution of disease exacerbation. Size fractionation of the serum revealed that a part of the IL-6 co-eluted with soluble gp130 and soluble IL-6 receptor. The IL-6-induced proliferation of murine B9 hybridoma was enhanced by recombinant soluble IL-6 receptor, whereas the proliferation was inhibited by recombinant soluble gp130. These results indicate that soluble gp130 may function as a natural inhibitor of the IL-6 actions in inflammatory bowel disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Soluble interleukin-6 receptors in inflammatory bowel disease: relation to circulating interleukin-6.Gut. 1995 Jan;36(1):45-9. doi: 10.1136/gut.36.1.45. Gut. 1995. PMID: 7890234 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor components sIL-6R and sgp130 as markers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018 Jul;33(7):927-936. doi: 10.1007/s00384-018-3069-8. Epub 2018 May 11. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2018. PMID: 29748708 Free PMC article.
-
Elevation of serum interleukin-6 but not serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor in children with Crohn's disease.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1996 Aug;23(2):164-71. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199608000-00012. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1996. PMID: 8856584 Clinical Trial.
-
Interleukin-6 biology is coordinated by membrane-bound and soluble receptors: role in inflammation and cancer.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Aug;80(2):227-36. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1105674. Epub 2006 May 17. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16707558 Review.
-
Targeting IL-13 as a Host-Directed Therapy Against Ulcerative Colitis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Nov 6;8:395. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00395. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30460209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous in vitro IL-6 production in various intestinal segments in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011 May;56(3):185-90. doi: 10.1007/s12223-011-0018-0. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2011. PMID: 21681687
-
Emerging therapeutic options in inflammatory bowel disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Dec 28;27(48):8242-8261. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i48.8242. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 35068868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of colitis-associated cancer: natural compounds that target the IL-6 soluble receptor.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012 Dec;12(10):1221-38. doi: 10.2174/187152012803833080. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22583410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-6 and its receptor: from bench to bedside.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2006 Dec;195(4):173-83. doi: 10.1007/s00430-006-0019-9. Epub 2006 May 31. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16741736 Review.
-
Interleukin-10 in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease: increased serum concentrations during the recovery phase.Mediators Inflamm. 2006;2006(6):26875. doi: 10.1155/MI/2006/26875. Mediators Inflamm. 2006. PMID: 17392581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Podolsky DK, Fiocchi C. Cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, eicosanoids, and other bioactive molecules in inflammatory bowel disease. In: Kirsner JB, editor. Inflammatory bowel disease. 5. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000. pp. 191–207.
-
- Cominelli F, Arseneau KO, Pizarro TT. The mucosal inflammatory response. Cytokines and chemokines. In: Targan SR, Shanahan F, Karp LC, editors. Inflammatory bowel disease: from bench to bedside. 2. Dordrecht, the Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2003. pp. 147–76.
-
- Mitsuyama K, Sata M, Tanikawa K. Significance of interleukin-6 in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1991;26:20–8. - PubMed
-
- Gross V, Andus T, Caesar I, Roth M, Scholmerich J. Evidence for continuous stimulation of interleukin-6 production in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1992;102:514–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

