The CD14 functional gene polymorphism -260 C>T is not involved in either the susceptibility to Chlamydia trachomatis infection or the development of tubal pathology
- PMID: 16368002
- PMCID: PMC1351185
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-5-114
The CD14 functional gene polymorphism -260 C>T is not involved in either the susceptibility to Chlamydia trachomatis infection or the development of tubal pathology
Abstract
Background: The functional polymorphism -260 C>T in the LPS sensing TLR4 co-receptor CD14 gene enhances the transcriptional activity and results in a higher CD14 receptor density. Individuals carrying the T/T genotype also have significantly higher serum levels of soluble CD14. The T allele of this polymorphism has recently been linked to Chlamydia pneumoniae infection. We investigated the role of the CD14 -260 C>T polymorphism in the susceptibility to and severity (defined as subfertility and/or tubal pathology) of C. trachomatis infection in Dutch Caucasian women.
Methods: The different CD14 -260 C>T genotypes were assessed by PCR-based RFLP analysis in three cohorts: 1) A cohort (n = 576) of women attending a STD clinic, 2) a cohort (n = 253) of women with subfertility, and 3) an ethnically matched control cohort (n = 170). The following variables were used in the analysis: In cohort 1 the CT-DNA status, CT IgG serology status, self-reported symptoms and in cohort 2, the CT IgG serology status and the tubal status at laparoscopy.
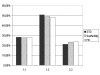
Results: In the control cohort the CC, CT and TT genotype distribution was: 28.2%, 48.2%, and 23.5% respectively. No differences were found in the overall prevalence of CD14 -260 genotypes (28.1%, 50.7%, and 21.2%) in cohort 1 when compared to the control cohort. Also no differences were observed in women with or without CT-DNA, with or without serological CT responses, with or without symptoms, or in combinations of these three variables. In subfertile women with tubal pathology (cohort 2, n = 50) the genotype distribution was 28.0%, 48.0%, and 24.0% and in subfertile women without tubal pathology (n = 203), 27.6%, 49.3% and 23.2%. The genotype distribution was unchanged when CT IgG status was introduced in the analyses.
Conclusion: The CD14 -260 C>T genotype distributions were identical in all three cohorts, showing that this polymorphism is not involved in the susceptibility to or severity of sequelae of C. trachomatis infection.
Figures
References
-
- Wira CR, Fahey JV, Sentman CL, Pioli PA, Shen L. Innate and adaptive immunity in female genital tract: cellular responses and interactions. Immunological Reviews. 2005 - PubMed
-
- Workowski KA, Stevens CE, Suchland RJ, Holmes KK, Eschenbach DA, Pettinger MB, Stamm WE. Clinical manifestations of genital infection due to Chlamydia trachomatis in women: differences related to serovar. Clin Infect Dis. 1994;19:756–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

