Involvement of claudin-7 in HIV infection of CD4(-) cells
- PMID: 16368003
- PMCID: PMC1352390
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-79
Involvement of claudin-7 in HIV infection of CD4(-) cells
Abstract
Background: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection of CD4(-) cells has been demonstrated, and this may be an important mechanism for HIV transmission.
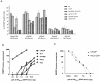
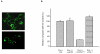
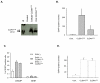
Results: We demonstrated that a membrane protein, claudin-7 (CLDN-7), is involved in HIV infection of CD4(-) cells. A significant increase in HIV susceptibility (2- to 100-fold) was demonstrated when CLDN-7 was transfected into a CD4(-) cell line, 293T. In addition, antibodies against CLDN-7 significantly decreased HIV infection of CD4(-) cells. Furthermore, HIV virions expressing CLDN-7 on their envelopes had a much higher infectivity for 293T CD4(-) cells than the parental HIV with no CLDN-7. RT-PCR results demonstrated that CLDN-7 is expressed in both macrophages and stimulated peripheral blood leukocytes, suggesting that most HIV virions generated in infected individuals have CLDN-7 on their envelopes. We also found that CLDN-7 is highly expressed in urogenital and gastrointestinal tissues.
Conclusion: Together these results suggest that CLDN-7 may play an important role in HIV infection of CD4(-) cells.
Figures
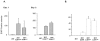

Similar articles
-
Regulation of the expression of the prostate-specific antigen by claudin-7.J Membr Biol. 2003 Aug 1;194(3):187-97. doi: 10.1007/s00232-003-2038-4. J Membr Biol. 2003. PMID: 14502431
-
Regulation of prostate-specific antigen expression by the junctional adhesion molecule A.Urology. 2009 May;73(5):1119-25. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2008.02.060. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Urology. 2009. PMID: 18602143
-
The claudin gene family: expression in normal and neoplastic tissues.BMC Cancer. 2006 Jul 12;6:186. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-186. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16836752 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the tight junction protein claudin-7 correlates with histological grade in both ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.Oncogene. 2003 Apr 3;22(13):2021-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206199. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12673207
-
Induction of lymphomonocyte activation by HIV-1 glycoprotein gp120. Possible role in AIDS pathogenesis.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1996 Oct-Dec;10(4):83-91. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1996. PMID: 9604776 Review.
Cited by
-
X chromosomal variation is associated with slow progression to AIDS in HIV-1-infected women.Am J Hum Genet. 2009 Aug;85(2):228-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.07.013. Am J Hum Genet. 2009. PMID: 19679225 Free PMC article.
-
Claudins in viral infection: from entry to spread.Pflugers Arch. 2017 Jan;469(1):27-34. doi: 10.1007/s00424-016-1908-4. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Pflugers Arch. 2017. PMID: 27885488 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral Disruption of Blood-Testis Barrier Precedes Testicular Infection.Viruses. 2025 May 23;17(6):747. doi: 10.3390/v17060747. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40573337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical functions of claudin proteins: Beyond the regulation of cell-cell adhesions.Tissue Barriers. 2017 Apr 3;5(2):e1327839. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2017.1327839. Epub 2017 May 19. Tissue Barriers. 2017. PMID: 28548895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Structural Protein GP3 Regulates Claudin 4 To Facilitate the Early Stages of Infection.J Virol. 2020 Sep 29;94(20):e00124-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00124-20. Print 2020 Sep 29. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32759320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dickerson MC, Johnston J, Delea TE, White A, Andrews E. The causal role for genital ulcer disease as risk factor for transmission of human immunodeficiency virus. Sex Transm Dis. 1996;23:429–440. - PubMed
-
- Miller CJ. Animal models of viral sexually transmitted diseases. Am J Reprod Immunol. 1994;31:52–63. - PubMed
-
- Miller CJ, Alexander NJ, Sutjipto S, Joye SM, Hendrickx AG, Jennings M, Marx PA. Effects of virus dose and nonoxynol-9 on the genital transmission of SIV in rhesus macaques. J Med Primatol. 1990;19:401–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

