Role of the luxS quorum-sensing system in biofilm formation and virulence of Staphylococcus epidermidis
- PMID: 16369005
- PMCID: PMC1346618
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.488-496.2006
Role of the luxS quorum-sensing system in biofilm formation and virulence of Staphylococcus epidermidis
Abstract
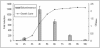
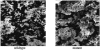
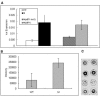
Nosocomial infections caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis are characterized by biofilm formation on implanted medical devices. Quorum-sensing regulation plays a major role in the biofilm development of many bacterial pathogens. Here, we describe luxS, a quorum-sensing system in staphylococci that has a significant impact on biofilm development and virulence. We constructed an isogenic DeltaluxS mutant strain of a biofilm-forming clinical isolate of S. epidermidis and demonstrated that luxS signaling is functional in S. epidermidis. The mutant strain showed increased biofilm formation in vitro and enhanced virulence in a rat model of biofilm-associated infection. Genetic complementation and addition of autoinducer 2-containing culture filtrate restored the wild-type phenotype, demonstrating that luxS repressed biofilm formation through a cell-cell signaling mechanism based on autoinducer 2 secretion. Enhanced production of the biofilm exopolysaccharide polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in the mutant strain is presumably the major cause of the observed phenotype. The agr quorum-sensing system has previously been shown to impact biofilm development and biofilm-associated infection in a way similar to that of luxS, although by regulation of different factors. Our study indicates a general scheme of quorum-sensing regulation of biofilm development in staphylococci, which contrasts with that observed in many other bacterial pathogens.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mutation in the S-ribosylhomocysteinase (luxS) gene involved in quorum sensing affects biofilm formation and virulence in a clinical isolate of Aeromonas hydrophila.Microb Pathog. 2008 Nov-Dec;45(5-6):343-54. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2008.08.007. Epub 2008 Sep 26. Microb Pathog. 2008. PMID: 18930130
-
Quorum-sensing control of biofilm factors in Staphylococcus epidermidis.J Infect Dis. 2003 Sep 1;188(5):706-18. doi: 10.1086/377239. Epub 2003 Aug 11. J Infect Dis. 2003. PMID: 12934187
-
Increased colonization of indwelling medical devices by quorum-sensing mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis in vivo.J Infect Dis. 2004 Oct 15;190(8):1498-505. doi: 10.1086/424487. Epub 2004 Sep 15. J Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15378444
-
Staphylococcus quorum sensing in biofilm formation and infection.Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Apr;296(2-3):133-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.01.042. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16487744 Review.
-
Quorum-sensing control in Staphylococci -- a target for antimicrobial drug therapy?FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004 Dec 15;241(2):135-41. doi: 10.1016/j.femsle.2004.11.016. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2004. PMID: 15598524 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic regulation of the intercellular adhesion locus in staphylococci.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Mar 26;2:38. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00038. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 23061050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agr system of Listeria monocytogenes EGD-e: role in adherence and differential expression pattern.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Oct;73(19):6125-33. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00608-07. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17675424 Free PMC article.
-
Interference in Bacterial Quorum Sensing: A Biopharmaceutical Perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 7;9:203. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00203. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29563876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SarZ is a key regulator of biofilm formation and virulence in Staphylococcus epidermidis.J Infect Dis. 2008 May 1;197(9):1254-62. doi: 10.1086/586714. J Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18422437 Free PMC article.
-
Staphylococcus epidermidis--the 'accidental' pathogen.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Aug;7(8):555-67. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2182. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19609257 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfaro, J. F., T. Zhang, D. P. Wynn, E. L. Karschner, and Z. S. Zhou. 2004. Synthesis of LuxS inhibitors targeting bacterial cell-cell communication. Org. Lett. 6:3043-3046. - PubMed
-
- Augustin, J., and F. Gotz. 1990. Transformation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and other staphylococcal species with plasmid DNA by electroporation. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 54:203-207. - PubMed
-
- Bassler, B. L., M. Wright, and M. R. Silverman. 1994. Multiple signalling systems controlling expression of luminescence in Vibrio harveyi: sequence and function of genes encoding a second sensory pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 13:273-286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

