IdeS, a highly specific immunoglobulin G (IgG)-cleaving enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes, is inhibited by specific IgG antibodies generated during infection
- PMID: 16369006
- PMCID: PMC1346671
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.497-503.2006
IdeS, a highly specific immunoglobulin G (IgG)-cleaving enzyme from Streptococcus pyogenes, is inhibited by specific IgG antibodies generated during infection
Abstract
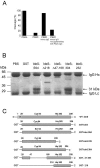
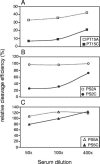
IdeS, a recently discovered cysteine proteinase secreted by the important human pathogen Streptococcus pyogenes, interferes with phagocytic killing by specifically cleaving the heavy chain of immunoglobulin G. The fact that the enzyme targets one of the key molecules of the adapted immune response raised the question of whether an antibody response against IdeS could inhibit, i.e., neutralize, enzyme activity. Paired acute- and convalescent-phase serum samples from patients with pharyngotonsillitis (n = 10), bacteremia (n = 7), and erysipelas (n = 4) were analyzed. Antibodies with the ability to neutralize IdeS enzymatic activity were already found in two-thirds of acute-phase sera. However, patients who seroconverted to IdeS, in particular patients with pharyngotonsillitis and erysipelas, developed specific antibodies during convalescence with an increased capability to efficiently neutralize the enzymatic activity of IdeS. Also, the presence of neutralizing antibodies decreased the ability of IdeS to mediate bacterial survival in human immune blood. In patients with bacteremia, several acute-phase sera contained neutralizing antibodies, but no correlation was found to severity or outcome of invasive infections. Still, the fact that the human immune response targets the enzymatic activity of IdeS supports the view that the enzyme plays an important role during streptococcal infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Enzymatic characterization of the streptococcal endopeptidase, IdeS, reveals that it is a cysteine protease with strict specificity for IgG cleavage due to exosite binding.Biochemistry. 2004 Dec 14;43(49):15540-9. doi: 10.1021/bi048284d. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15581366
-
The streptococcal protease IdeS modulates bacterial IgGFc binding and generates 1/2Fc fragments with the ability to prime polymorphonuclear leucocytes.Mol Immunol. 2008 Jul;45(12):3347-53. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.04.013. Epub 2008 Jun 3. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18533265
-
Proteolytic processing of the streptococcal IgG endopeptidase IdeS modulates the functional properties of the enzyme and results in reduced immunorecognition.Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt A):176-84. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.07.014. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26343448
-
Streptococcal IdeS and its impact on immune response and inflammation.J Innate Immun. 2012;4(2):132-40. doi: 10.1159/000332940. Epub 2012 Jan 17. J Innate Immun. 2012. PMID: 22248585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IdeS and SpeB: immunoglobulin-degrading cysteine proteinases of Streptococcus pyogenes.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003 Feb;6(1):50-5. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(03)00003-1. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12615219 Review.
Cited by
-
The intrinsic immunoglobulin g endopeptidase activity of streptococcal Mac-2 proteins implies a unique role for the enzymatically impaired Mac-2 protein of M28 serotype strains.Infect Immun. 2008 May;76(5):2183-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01422-07. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18332209 Free PMC article.
-
IdeS: a bacterial proteolytic enzyme with therapeutic potential.PLoS One. 2008 Feb 27;3(2):e1692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001692. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18301769 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomic analysis of natural selection pressure in Streptococcus genomes.BMC Evol Biol. 2007 Aug 30;7:154. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-154. BMC Evol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17760998 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus pyogenes Infection and the Human Proteome with a Special Focus on the Immunoglobulin G-cleaving Enzyme IdeS.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018 Jun;17(6):1097-1111. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA117.000525. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29511047 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Engineering and characterization of the chimeric antibody that targets the C-terminal telopeptide of the α2 chain of human collagen I: a next step in the quest to reduce localized fibrosis.Connect Tissue Res. 2013;54(3):187-96. doi: 10.3109/03008207.2013.778839. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Connect Tissue Res. 2013. PMID: 23586407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agniswamy, J., B. Lei, J. M. Musser, and P. D. Sun. 2004. Insight of host immune evasion mediated by two variants of group A streptococcus Mac protein. J. Biol. Chem. 279:52789-52796. - PubMed
-
- Åkesson, P., A. Linder, J. Cronqvist, and B. Christensson. 2004. Group A Streptococcus bacteraemia complicated by osteomyelitis in an immunocompetent adult. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 36:63-65. - PubMed
-
- Åkesson, P., M. Rasmussen, E. Mascini, U. von Pawel-Rammingen, R. Janulczyk, M. Collin, A. Olsén, E. Mattsson, M. L. Olsson, L. Björck, and B. Christensson. 2004. Low antibody titers to cell wall-attached proteins of Streptococcus pyogenes predispose for severe invasive disease. J. Infect. Dis. 189:797-804. - PubMed
-
- Beall, B., R. Facklam, T. Hoenes, and B. Schwartz. 1997. Survey of emm gene sequences and T-antigen types from systemic Streptococcus pyogenes infection isolates collected in San Francisco, California; Atlanta, Georgia; and Connecticut in 1994 and 1995. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:1231-1235. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

