Virulence of broad- and narrow-host-range Salmonella enterica serovars in the streptomycin-pretreated mouse model
- PMID: 16369020
- PMCID: PMC1346614
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.632-644.2006
Virulence of broad- and narrow-host-range Salmonella enterica serovars in the streptomycin-pretreated mouse model
Abstract
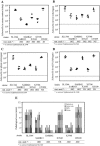
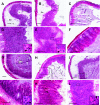
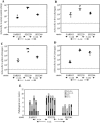
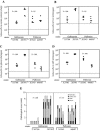
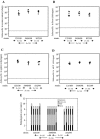
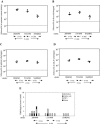
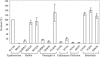
Salmonella enterica subspecies I serovars are common bacterial pathogens causing diseases ranging from enterocolitis to systemic infections. Some serovars are adapted to specific hosts, whereas others have a broad host range. The molecular mechanisms defining the virulence characteristics and the host range of a given S. enterica serovar are unknown. Streptomycin pretreated mice provide a surrogate host model for studying molecular aspects of the intestinal inflammation (colitis) caused by serovar Typhimurium (S. Hapfelmeier and W. D. Hardt, Trends Microbiol. 13:497-503, 2005). Here, we studied whether this animal model is also useful for studying other S. enterica subspecies I serovars. All three tested strains of the broad-host-range serovar Enteritidis (125109, 5496/98, and 832/99) caused pronounced colitis and systemic infection in streptomycin pretreated mice. Different levels of virulence were observed among three tested strains of the host-adapted serovar Dublin (SARB13, SD2229, and SD3246). Several strains of host restricted serovars were also studied. Two serovar Pullorum strains (X3543 and 449/87) caused intermediate levels of colitis. No intestinal inflammation was observed upon infection with three different serovar Paratyphi A strains (SARB42, 2804/96, and 5314/98) and one serovar Gallinarum strain (X3796). A second serovar Gallinarum strain (287/91) was highly virulent and caused severe colitis. This strain awaits future analysis. In conclusion, the streptomycin pretreated mouse model can provide an additional tool to study virulence factors (i.e., those involved in enteropathogenesis) of various S. enterica subspecies I serovars. Five of these strains (125109, 2229, 287/91, 449/87, and SARB42) are subject of Salmonella genome sequencing projects. The streptomycin pretreated mouse model may be useful for testing hypotheses derived from this genomic data.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium pathogenicity island 2 is necessary for complete virulence in a mouse model of infectious enterocolitis.Infect Immun. 2005 Jun;73(6):3219-27. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3219-3227.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15908346 Free PMC article.
-
Haemolysins of Salmonella, their role in pathogenesis and subtyping of Salmonella serovars.Indian J Exp Biol. 2004 Mar;42(3):303-13. Indian J Exp Biol. 2004. PMID: 15233302
-
Inactivation of ppk differentially affects virulence and disrupts ATP homeostasis in Salmonella enterica serovars Typhimurium and Gallinarum.Res Microbiol. 2007 Jan-Feb;158(1):79-85. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2006.10.008. Epub 2006 Dec 19. Res Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17227702
-
Salmonella pathogenicity islands in host specificity, host pathogen-interactions and antibiotics resistance of Salmonella enterica.Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007 Jul-Aug;120(7-8):317-27. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2007. PMID: 17715824 Review.
-
[Virulence plasmids of Salmonella enterica--incidence and properties].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2005 Jan-Feb;118(1-2):8-23. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2005. PMID: 15690632 Review. German.
Cited by
-
A novel phage element of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis P125109 contributes to accelerated type III secretion system 2-dependent early inflammation kinetics in a mouse colitis model.Infect Immun. 2012 Sep;80(9):3236-46. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00180-12. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Infect Immun. 2012. PMID: 22753379 Free PMC article.
-
Animal Models for Salmonellosis: Applications in Vaccine Research.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016 Sep 6;23(9):746-56. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00258-16. Print 2016 Sep. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27413068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella Typhimurium TTSS-2 deficient mig-14 mutant shows attenuation in immunocompromised mice and offers protection against wild-type Salmonella Typhimurium infection.BMC Microbiol. 2013 Oct 22;13:236. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-13-236. BMC Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24148706 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated type III secretion system 2-dependent enteropathogenesis by a Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis PT4/6 strain.Infect Immun. 2009 Sep;77(9):3569-77. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00511-09. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19528213 Free PMC article.
-
Host specificity of bacterial pathogens.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013 Dec 1;3(12):a010041. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010041. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2013. PMID: 24296346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Barrow, P. A., M. B. Huggins, M. A. Lovell, and J. M. Simpson. 1987. Observations on the pathogenesis of experimental Salmonella typhimurium infection in chickens. Res. Vet. Sci. 42:194-199. - PubMed
-
- Barthel, M., S. Hapfelmeier, L. Quintanilla-Martinez, M. Kremer, M. Rohde, M. Hogardt, K. Pfeffer, H. Russmann, and W. D. Hardt. 2003. Pretreatment of mice with streptomycin provides a Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium colitis model that allows analysis of both pathogen and host. Infect. Immun. 71:2839-2858. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

