Platelets potentiate brain endothelial alterations induced by Plasmodium falciparum
- PMID: 16369021
- PMCID: PMC1346683
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.74.1.645-653.2006
Platelets potentiate brain endothelial alterations induced by Plasmodium falciparum
Abstract
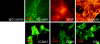
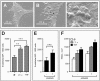
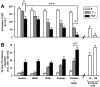
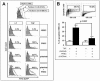
Brain lesions of cerebral malaria (CM) are characterized by a sequestration of Plasmodium falciparum-parasitized red blood cells (PRBC) and platelets within brain microvessels, as well as by blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption. In the present study, we evaluated the possibility that PRBC and platelets induce functional alterations in brain endothelium. In a human brain endothelial cell line, named HBEC-5i, exhibiting most of the features demanded for a pathophysiological study of BBB, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) or lymphotoxin alpha (LT-alpha) reduced transendothelial electrical resistance (TEER), enhanced the permeability to 70-kDa dextran, and increased the release of microparticles, a recently described indicator of disease severity in CM patients. In vitro cocultures showed that platelets or PRBC can have a direct cytotoxic effect on activated, but not on resting, HBEC-5i cells. Platelet binding was required, as platelet supernatant had no effect. Furthermore, platelets potentiated the cytotoxicity of PRBC for TNF- or LT-alpha-activated HBEC-5i cells when they were added prior to these cells on the endothelial monolayers. This effect was not observed when platelets were added after PRBC. Both permeability and TEER were strongly affected, and the apoptosis rate of HBEC-5i cells was dramatically increased. These findings provide insights into the mechanisms by which platelets can be deleterious to the brain endothelium during CM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cerebral malaria: role of microparticles and platelets in alterations of the blood-brain barrier.Int J Parasitol. 2006 May 1;36(5):541-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Int J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16600245 Review.
-
Selection of Plasmodium falciparum parasites for cytoadhesion to human brain endothelial cells.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jan 3;(59):e3122. doi: 10.3791/3122. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22230803 Free PMC article.
-
A simple protocol for platelet-mediated clumping of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes in a resource poor setting.J Vis Exp. 2013 May 16;(75):e4316. doi: 10.3791/4316. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 23711755 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet microparticles: a new player in malaria parasite cytoadherence to human brain endothelium.FASEB J. 2009 Oct;23(10):3449-58. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-135822. Epub 2009 Jun 17. FASEB J. 2009. PMID: 19535685
-
Platelet-endothelial cell interactions in cerebral malaria: the end of a cordial understanding.Thromb Haemost. 2009 Dec;102(6):1093-102. doi: 10.1160/TH09-05-0337. Thromb Haemost. 2009. PMID: 19967139 Review.
Cited by
-
P. falciparum isolate-specific distinct patterns of induced apoptosis in pulmonary and brain endothelial cells.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 31;9(3):e90692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090692. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24686750 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Culture Models: Key Players in In Vitro Neurotoxicity, Neurodegeneration and BBB Modeling Studies.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 12;12(3):626. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030626. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoadherence and severe malaria.Malays J Med Sci. 2012 Apr;19(2):5-18. Malays J Med Sci. 2012. PMID: 22973133 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay of Plasmodium falciparum and thrombin in brain endothelial barrier disruption.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 11;9(1):13142. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49530-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31511575 Free PMC article.
-
von Willebrand factor in experimental malaria-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome.J Thromb Haemost. 2019 Aug;17(8):1372-1383. doi: 10.1111/jth.14485. Epub 2019 Jun 12. J Thromb Haemost. 2019. PMID: 31099973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ades, E. W., F. J. Candal, R. A. Swerlick, V. G. George, S. Summers, D. C. Bosse, and T. J. Lawley. 1992. HMEC-1: establishment of an immortalized human microvascular endothelial cell line. J. Investig. Dermatol. 99:683-690. - PubMed
-
- Aikawa, M., E. Pongponratn, T. Tegoshi, K. Nakamura, T. Nagatake, A. Cochrane, and L. S. Ozaki. 1992. A study on the pathogenesis of human cerebral malaria and cerebral babesiosis. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 87(Suppl. 3):297-301. - PubMed
-
- Belloni, P. N., and R. J. Tressler. 1990. Microvascular endothelial cell heterogeneity: interactions with leukocytes and tumor cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 8:353-389. - PubMed
-
- Berendt, A. R., D. J. Ferguson, J. Gardner, G. Turner, A. Rowe, C. McCormick, D. Roberts, A. Craig, R. Pinches, B. C. Elford, et al. 1994. Molecular mechanisms of sequestration in malaria. Parasitology 108(Suppl.):S19-S28. - PubMed
-
- Bevilacqua, M. P., and M. A. Gimbrone, Jr. 1987. Inducible endothelial functions in inflammation and coagulation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 13:425-433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

