Umbilical cord blood procalcitonin and C reactive protein concentrations as markers for early diagnosis of very early onset neonatal infection
- PMID: 16371391
- PMCID: PMC2672656
- DOI: 10.1136/adc.2005.074245
Umbilical cord blood procalcitonin and C reactive protein concentrations as markers for early diagnosis of very early onset neonatal infection
Abstract
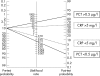
Procalcitonin (PCT) and C reactive protein (CRP) concentrations in umbilical cord blood of 197 neonates were measured to evaluate their value as markers of infection. Sixteen of the neonates were infected. The sensitivity, specificity, and negative and positive predictive values were respectively 87.5%, 98.7%, 87.5%, and 98.7% for PCT and 50%, 97%, 67%, and 94% for CRP. Serum PCT in cord blood seems to be a useful and early marker of antenatal infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
Similar articles
-
[Interleukin-6, procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and the immature to total neutrophil ratio (I/T) in the diagnosis of early-onset sepsis in low birth weight neonates].Ceska Gynekol. 2000 Dec;65 Suppl 1:29-33. Ceska Gynekol. 2000. PMID: 11394228 Czech.
-
[Diagnostic value of suspicion criteria for early-onset neonatal bacterial infection: report ten years after the Anaes recommendations].Arch Pediatr. 2014 Feb;21(2):187-93. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2013.11.011. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Arch Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 24411567 French.
-
Umbilical cord blood serum procalcitonin by Time-Resolved Amplified Cryptate Emission (TRACE) technology: reference values of a potential marker of vertically transmitted neonatal sepsis.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007;45(11):1531-5. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2007.304. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2007. PMID: 17892436
-
Procalcitonin as an early marker of infection in neonates and children.Lancet Infect Dis. 2004 Oct;4(10):620-30. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(04)01146-6. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15451490 Review.
-
Usefulness of estimation of blood procalcitonin concentration versus C-reactive protein concentration and white blood cell count for therapeutic monitoring of sepsis in neonates.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014 Dec 21;68:1516-23. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1133101. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2014. PMID: 25531715 Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal serum ferritin concentration is positively associated with newborn iron stores in women with low ferritin status in late pregnancy.J Nutr. 2012 Nov;142(11):2004-9. doi: 10.3945/jn.112.162362. Epub 2012 Sep 26. J Nutr. 2012. PMID: 23014493 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping prenatal predictors and neurobehavioral outcomes of an epigenetic marker of neonatal inflammation - A longitudinal population-based study.Brain Behav Immun. 2024 Nov;122:483-496. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.08.053. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Brain Behav Immun. 2024. PMID: 39209009 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for diagnosis of neonatal infections: A systematic analysis of their potential as a point-of-care diagnostics.J Glob Health. 2011 Dec;1(2):201-9. J Glob Health. 2011. PMID: 23198119 Free PMC article.
-
Umbilical cord blood procalcitonin level in early neonatal infections: a 4-year university hospital cohort study.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 Aug;30(8):1005-13. doi: 10.1007/s10096-011-1187-0. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21311939
-
Early-onset neonatal sepsis in the Paris area: a population-based surveillance study from 2019 to 2021.Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2023 Mar;108(2):114-120. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2022-324080. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2023. PMID: 35902218 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous