Rapid, diffusional shuttling of poly(A) RNA between nuclear speckles and the nucleoplasm
- PMID: 16371503
- PMCID: PMC1382313
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-10-0952
Rapid, diffusional shuttling of poly(A) RNA between nuclear speckles and the nucleoplasm
Abstract
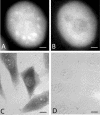
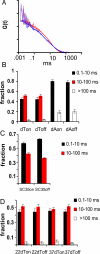
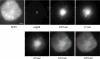
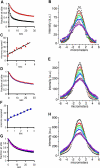
Speckles are nuclear bodies that contain pre-mRNA splicing factors and polyadenylated RNA. Because nuclear poly(A) RNA consists of both mRNA transcripts and nucleus-restricted RNAs, we tested whether poly(A) RNA in speckles is dynamic or rather an immobile, perhaps structural, component. Fluorescein-labeled oligo(dT) was introduced into HeLa cells stably expressing a red fluorescent protein chimera of the splicing factor SC35 and allowed to hybridize. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) showed that the mobility of the tagged poly(A) RNA was virtually identical in both speckles and at random nucleoplasmic sites. This same result was observed in photoactivation-tracking studies in which caged fluorescein-labeled oligo(dT) was used as hybridization probe, and the rate of movement away from either a speckle or nucleoplasmic site was monitored using digital imaging microscopy after photoactivation. Furthermore, the tagged poly(A) RNA was observed to rapidly distribute throughout the entire nucleoplasm and other speckles, regardless of whether the tracking observations were initiated in a speckle or the nucleoplasm. Finally, in both FCS and photoactivation-tracking studies, a temperature reduction from 37 to 22 degrees C had no discernible effect on the behavior of poly(A) RNA in either speckles or the nucleoplasm, strongly suggesting that its movement in and out of speckles does not require metabolic energy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tracking nuclear poly(A) RNA movement within and among speckle nuclear bodies and the surrounding nucleoplasm.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1042:61-71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-526-2_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23980000
-
Identification of a chemical inhibitor for nuclear speckle formation: implications for the function of nuclear speckles in regulation of alternative pre-mRNA splicing.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Mar 28;446(1):119-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.060. Epub 2014 Feb 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24569078
-
Poly(A)+ RNAs roam the cell nucleus and pass through speckle domains in transcriptionally active and inactive cells.J Cell Biol. 2004 Apr 26;165(2):191-202. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200310139. J Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15117966 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;4(8):605-12. doi: 10.1038/nrm1172. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12923522 Review.
-
Nuclear speckles.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Feb 1;3(2):a000646. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000646. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 20926517 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncoupling of nucleo-cytoplasmic RNA export and localization during stress.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 May 21;47(9):4778-4797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz168. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30864659 Free PMC article.
-
Single-molecule dynamics of nuclear mRNA.F1000 Biol Rep. 2009 Apr 29;1:29. doi: 10.3410/B1-29. F1000 Biol Rep. 2009. PMID: 20948657 Free PMC article.
-
Differential dynamics of splicing factor SC35 during the cell cycle.J Biosci. 2008 Sep;33(3):345-54. doi: 10.1007/s12038-008-0054-3. J Biosci. 2008. PMID: 19005234
-
Splicing regulation through biomolecular condensates and membraneless organelles.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024 Sep;25(9):683-700. doi: 10.1038/s41580-024-00739-7. Epub 2024 May 21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38773325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol- and PARP-Mediated Regulation of Ribosome-Associated Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) in Pyramidal Neurons.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Nov 17;9(6):72. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9060072. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37987368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bubulya, P. A., and Spector, D. L. (2004). “On the move”ments of nuclear components in living cells. Exp. Cell Res. 296, 4–11. - PubMed
-
- Cardullo, R. A., Mungovan, R. M., and Wolf, D. E. (1991). Imaging membrane organization and dynamics. In: Biophysical and Biochemical Aspects of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, ed. T. D. Dewey, New York: Plenum Publishing, 231–260.
-
- Carrington, W. A., Lynch, R. M., Moore, E. D., Isenberg, G., Fogarty, K. E., and Fay, F. S. (1995). Superresolution three-dimensional images of fluorescence in cells with minimal light exposure. Science 268, 1483–1487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

