Shiga toxin regulates its entry in a Syk-dependent manner
- PMID: 16371508
- PMCID: PMC1382301
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0766
Shiga toxin regulates its entry in a Syk-dependent manner
Abstract
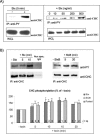
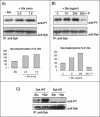
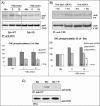
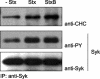
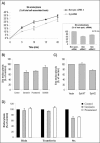
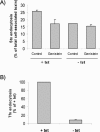
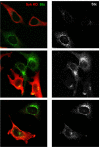
Shiga toxin (Stx) is composed of an A-moiety that inhibits protein synthesis after translocation into the cytosol, and a B-moiety that binds to Gb3 at the cell surface and mediates endocytosis of the toxin. After endocytosis, Stx is transported retrogradely to the endoplasmic reticulum, and then the A-fragment enters the cytosol. In this study, we have investigated whether toxin-induced signaling is involved in its entry. Stx was found to activate Syk and induce rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of several proteins, one protein being clathrin heavy chain. Toxin-induced clathrin phosphorylation required Syk activity, and in cells overexpressing Syk, a complex containing clathrin and Syk could be demonstrated. Depletion of Syk by small interfering RNA, expression of a dominant negative Syk mutant (Syk KD), or treatment with the Syk inhibitor piceatannol inhibited not only Stx-induced clathrin phosphorylation but also endocytosis of the toxin. Also, Golgi transport of Stx was inhibited under all these conditions. In conclusion, our data suggest that Stx regulates its entry into target cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of clathrin and Syk interaction upon Shiga toxin binding.Cell Signal. 2009 Jul;21(7):1161-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.03.005. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19289168
-
Shiga toxin increases formation of clathrin-coated pits through Syk kinase.PLoS One. 2010 Jul 27;5(7):e10944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010944. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20668539 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient endosome-to-Golgi transport of Shiga toxin is dependent on dynamin and clathrin.J Cell Sci. 2004 May 1;117(Pt 11):2321-31. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01081. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15126632
-
Endocytosis and retrograde transport of Shiga toxin.Toxicon. 2010 Dec 15;56(7):1181-5. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2009.11.021. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 19951719 Review.
-
Pathways followed by ricin and Shiga toxin into cells.Histochem Cell Biol. 2002 Feb;117(2):131-41. doi: 10.1007/s00418-001-0346-2. Epub 2001 Nov 20. Histochem Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 11935289 Review.
Cited by
-
Shiga toxin (Stx)1B and Stx2B induce von Willebrand factor secretion from human umbilical vein endothelial cells through different signaling pathways.Blood. 2011 Sep 22;118(12):3392-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-06-363648. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21816831 Free PMC article.
-
Endosomal trafficking of the ligated FcvarepsilonRI receptor.Mol Immunol. 2009 Feb;46(5):793-802. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.09.002. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Mol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 18945491 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of apoptosis by Shiga toxins.Future Microbiol. 2010 Mar;5(3):431-53. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.4. Future Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20210553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Annexin A1 and A2: roles in retrograde trafficking of Shiga toxin.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040429. Epub 2012 Jul 6. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22792315 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the Classical Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases Is Part of the Shiga Toxin-Induced Ribotoxic Stress Response and May Contribute to Shiga Toxin-Induced Inflammation.Infect Immun. 2015 Oct 19;84(1):138-48. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00977-15. Print 2016 Jan. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 26483408 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

