Imaging of serotonin mechanisms in epilepsy
- PMID: 16372050
- PMCID: PMC1312732
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2005.00064.x
Imaging of serotonin mechanisms in epilepsy
Abstract
Advances in positron emission tomography (PET) techniques have allowed the measurement and imaging of neurotransmitter synthesis, transport, and receptor binding to be performed in vivo. With regard to epileptic disorders, imaging of neurotransmitter systems not only assists in the identification of epileptic foci for surgical treatment, but also provides insights into the basic mechanisms of human epilepsy. Recent investigative interest in epilepsy has focused on PET imaging of tryptophan metabolism, via the serotonin and kynurenine pathways, as well as on imaging of serotonin receptors. This review summarizes advances in PET imaging and how these techniques can be applied clinically for epilepsy treatment.
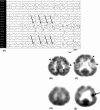
Figures
References
-
- Dailey JW, Reigel CE, Mishra PK, Jobe PC. Neurobiology of seizure predisposition in the genetically epilepsy-prone rat. Epilepsy Res. 1989;3:317–320. - PubMed
-
- Statnick MA, Dailey JW, Jobe PC, Browning RA. Abnormalities in brain serotonin concentration, high-affinity uptake, and tryptophan hydroxylase activity in severe-seizure genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Epilepsia. 1996;37:311–321. - PubMed
-
- Wenger GR, Stitzel RE, Craig CR. The role of biogenic amines in the reserpine-induced alteration of minimal electroshock seizure thresholds in the mouse. Neuropharmacology. 1973;12:693–703. - PubMed
-
- Lazarova M, Bendotti C, Samanin R. Studies on the role of serotonin in different regions of the rat central nervous system on pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures and the effect of Di-n-propyl-acetate. Arch Pharmacol. 1983;322:147–152. - PubMed
-
- Maynert E, Marczynski T, Browning R. The role of neurotransmitters in the epilepsies. Adv Neurol. 1975;13:79–147. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

