Silent plateau potentials, rhythmic bursts, and pacemaker firing: three patterns of activity that coexist in quadristable subthalamic neurons
- PMID: 16373507
- PMCID: PMC1324981
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0506781102
Silent plateau potentials, rhythmic bursts, and pacemaker firing: three patterns of activity that coexist in quadristable subthalamic neurons
Abstract
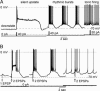
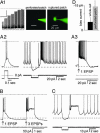
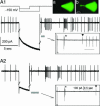
Subthalamic neurons display uncommon intrinsic behaviors that are likely to contribute to the motor and cognitive functions of the basal ganglia and to many of its disorders. Here, we report silent plateau potentials in these cells. These plateau responses start with a transient burst of action potentials that quickly diminish in amplitude because of spike inactivation and current shunt. The resulting interruption of spiking reveals a stable depolarization (up state) that clamps the cell membrane potential near -40 mV for several seconds. These plateau potentials coexist in single subthalamic neurons with more familiar patterns of burst and pacemaker firing. Within a narrow range of baseline membrane potentials (-67 to -60 mV), depolarization abruptly switches single cells from bistable to rhythmic bursts or tonic firing modes, thus selecting entirely distinct algorithms for integrating cortical and pallidal synaptic inputs.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Slowly inactivating sodium current (I(NaP)) underlies single-spike activity in rat subthalamic neurons.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Apr;83(4):1951-7. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.83.4.1951. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10758106
-
Excitatory postsynaptic potentials trigger a plateau potential in rat subthalamic neurons at hyperpolarized states.J Neurophysiol. 2001 Oct;86(4):1816-25. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.86.4.1816. J Neurophysiol. 2001. PMID: 11600642
-
Orexin-induced modulation of state-dependent intrinsic properties in thalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons attenuates action potential patterning and frequency.Neuroscience. 2007 Jul 29;147(4):1066-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.05.018. Epub 2007 Jun 28. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17600629
-
GABAergic control of the subthalamic nucleus.Prog Brain Res. 2007;160:173-88. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)60010-1. Prog Brain Res. 2007. PMID: 17499114 Review.
-
[The pacemaker of dominating motivation].Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 1992 Dec;78(12):1-11. Fiziol Zh Im I M Sechenova. 1992. PMID: 1306743 Review. Russian. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Subthalamic Nucleus becomes a Generator of Bursts in the Dopamine-Depleted State. Its High Frequency Stimulation Dramatically Weakens Transmission to the Globus Pallidus.Front Syst Neurosci. 2011 Jun 13;5:43. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2011.00043. eCollection 2011. Front Syst Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21716635 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Working Memory in a Spiking Neuron Network Accompanied by Astrocytes.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Mar 31;15:631485. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.631485. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33867939 Free PMC article.
-
Ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channels: what's all the buzz about?Schizophr Bull. 2007 Nov;33(6):1263-9. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbm106. Epub 2007 Sep 28. Schizophr Bull. 2007. PMID: 17905786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multistable properties of human subthalamic nucleus neurons in Parkinson's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Nov 26;116(48):24326-24333. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1912128116. Epub 2019 Nov 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31712414 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of 5-HT neuron activity and induction of depressive-like behavior by high-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Oct 23;104(43):17087-92. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704144104. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17942692 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamani, C., Saint-Cyr, J. A., Fraser, J., Kaplitt, M. & Lozano, A. M. (2004) Brain 127, 4–20. - PubMed
-
- Wichmann, T. & DeLong, M. R. (2003) Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 991, 199–213. - PubMed
-
- Mallet, L., Mesnage, V., Houeto, J. L., Pelissolo, A., Yelnik, J., Behar, C., Gargiulo, M., Welter, M. L., Bonnet, A. M., Pillon, B., et al. (2002) Lancet 360, 1302–1304. - PubMed
-
- Baunez, C., Dias, C., Cador, M. & Amalric, M. (2005) Nat. Neurosci. 8, 484–489. - PubMed
-
- Limousin, P., Krack, P., Pollak, P., Benazzouz, A., Ardouin, C., Hoffmann, D. & Benabid, A. L. (1998) N. Engl. J. Med. 339, 1105–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

