Gadobenate dimeglumine as an intrabiliary contrast agent: comparison with mangafodipir trisodium with respect to non-dilated biliary tree depiction
- PMID: 16374080
- PMCID: PMC2684969
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2005.6.4.229
Gadobenate dimeglumine as an intrabiliary contrast agent: comparison with mangafodipir trisodium with respect to non-dilated biliary tree depiction
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy of Mangafodipir trisodium (Mn-DPDP)-enhanced MR cholangiogrphy (MRC) and Gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA)-enhanced MRC in visualizing a non-dilated biliary system.
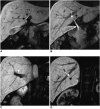
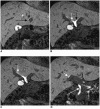
Materials and methods: Eighty-eight healthy liver donor candidates underwent contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRC. Mn-DPDP and Gd-BOPTA was used in 36 and 52 patients, respectively. Two radiologists reviewed the MR images and rated the visualization of the common duct, the right and left hepatic ducts, and the second-order branches using a 4-point scale. The contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) of the common duct to the liver in the two groups was also compared.
Results: Mn-DPDP MRC and Gd-BOPTA MRC both showed similar visualization grades in the common duct (p=.380, Mann-Whitney U test). In the case of the proximal bile ducts, the median visualization grade was significantly higher with Gd-BOPTA MRC than with Mn-DPDP MRC (right hepatic duct: p=0.016, left hepatic duct: p=0.014, right secondary order branches: p=0.006, left secondary order branches, p=0.003). The common duct-to-liver CNR of the Gd-BOPTA MRC group was significantly higher (38.90+/-24.50) than that of the Mn-DPDP MRC group (24.14+/-17.98) (p=.003, Student's t test).
Conclusion: Gd-BOPTA, as a biliary contrast agent, is a potential substitute for Mn-DPDP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contrast-enhanced MR cholangiography: comparison of Gd-EOB-DTPA and Mn-DPDP in healthy volunteers.Br J Radiol. 2012 Sep;85(1017):1250-4. doi: 10.1259/bjr/22238911. Epub 2012 May 2. Br J Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22553292 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative evaluation of biliary anatomy in adult live liver donors with volumetric mangafodipir trisodium enhanced magnetic resonance cholangiography.Liver Transpl. 2004 Nov;10(11):1391-7. doi: 10.1002/lt.20281. Liver Transpl. 2004. PMID: 15497156
-
Hepatobiliary-specific MR contrast agents: role in imaging the liver and biliary tree.Radiographics. 2009 Oct;29(6):1725-48. doi: 10.1148/rg.296095515. Radiographics. 2009. PMID: 19959518
-
Mangafodipir trisodium injection (Mn-DPDP). A contrast agent for abdominal MR imaging.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1996 Feb;4(1):73-85. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1996. PMID: 8673718 Review.
-
Hepatobiliary contrast agents for contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver: properties, clinical development and applications.Eur Radiol. 2004 Apr;14(4):559-78. doi: 10.1007/s00330-004-2236-1. Epub 2004 Feb 25. Eur Radiol. 2004. PMID: 14986050 Review.
Cited by
-
A serial dilution study of gadolinium-based MR imaging contrast agents.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008 Apr;29(4):668-73. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A0905. Epub 2008 Jan 9. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. PMID: 18184840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takehara Y. Fast MR imaging for evaluating the pancreaticobiliary system. Eur J Radiol. 1999;29:211–232. - PubMed
-
- Irie H, Honda H, Tajima T, Kuroiwa T, Yoshimitsu K, Makisumi K, et al. Optimal MR cholangiopancreatographic sequence and its clinical application. Radiology. 1998;206:379–387. - PubMed
-
- Fulcher AS, Turner MA, Capps GW, Zfass AM, Baker KM. Half-Fourier RARE MR cholangiopancreatography: experience in 300 subjects. Radiology. 1998;207:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Hintze RE, Adler A, Veltzke W, Abou-Rebyeh H, Hammerstingl R, Vogl T, et al. Clinical significance of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) compared to endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopy. 1997;29:182–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

