Yeast Trf5p is a nuclear poly(A) polymerase
- PMID: 16374505
- PMCID: PMC1369253
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400612
Yeast Trf5p is a nuclear poly(A) polymerase
Abstract
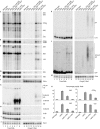
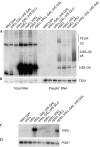
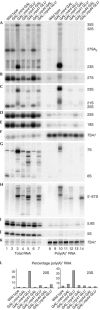
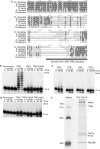
Recent analyses have shown that the activity of the yeast nuclear exosome is stimulated by the Trf4p-Air1/2p-Mtr4p polyadenylation (TRAMP) complex. Here, we report that strains lacking the Rrp6p component of the nuclear exosome accumulate polyadenylated forms of many different ribosomal RNA precursors (pre-rRNAs). This polyadenylation is reduced in strains lacking either the poly(A) polymerase Trf4p or its close homologue Trf5p. In contrast, polyadenylation is enhanced by overexpression of Trf5p. Polyadenylation is also markedly increased in strains lacking the RNA helicase Mtr4p, indicating that it is required to couple poly(A) polymerase activity to degradation. Tandem affinity purification-tagged purified Trf5p showed polyadenylation activity in vitro, which was abolished by a double point mutation in the predicted catalytic site. Trf5p co-purified with Mtr4p and Air1p, indicating that it forms a complex, designated TRAMP5, that has functions that partially overlap with the TRAMP complex.
Figures
References
-
- Bousquet-Antonelli C, Presutti C, Tollervey D (2000) Identification of a regulated pathway for nuclear pre-mRNA turnover. Cell 102: 765–775 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

