Adipose triglyceride lipase: function, regulation by insulin, and comparison with adiponutrin
- PMID: 16380488
- PMCID: PMC2819178
Adipose triglyceride lipase: function, regulation by insulin, and comparison with adiponutrin
Abstract
Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) is a recently described adipose-enriched protein with triglyceride-specific lipase activity. ATGL shares the greatest sequence homology with adiponutrin, a nutritionally regulated protein of unclear biological function. Here we present a functional analysis of ATGL and adiponutrin and describe their regulation by insulin. Retroviral-mediated overexpression of ATGL in 3T3-L1 adipocytes increased basal and isoproterenol-stimulated glycerol and nonesterified fatty acid (NEFA) release, whereas siRNA-mediated knockdown of ATGL had the opposite effect. In contrast, siRNA-mediated knockdown of adiponutrin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes had no effect on glycerol or NEFA release. In mice, both ATGL and adiponutrin are nutritionally regulated in adipose tissue, with ATGL being upregulated and adiponutrin being downregulated by fasting. In 3T3-L1 adipocytes, insulin decreased ATGL and increased adiponutrin expression in a dose- and time-dependent manner, suggesting that insulin directly mediates this nutritional regulation. In addition, adipose expression of ATGL was increased by insulin deficiency and decreased by insulin replacement in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice and was increased in fat-specific insulin receptor knockout mice, whereas adiponutrin showed the opposite pattern. These data suggest that murine ATGL but not adiponutrin contributes to net adipocyte lipolysis and that ATGL and adiponutrin are oppositely regulated by insulin both in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
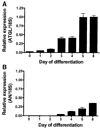
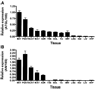
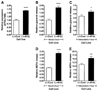
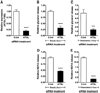
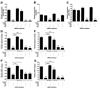
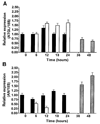
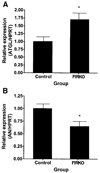
 ) (n = 10 per group) with the onset of the light cycle (6:00
) (n = 10 per group) with the onset of the light cycle (6:00 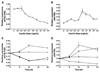
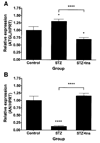
References
-
- Holm C. Molecular mechanisms regulating hormone-sensitive lipase and lipolysis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:1120–1124. - PubMed
-
- Kraemer FB, Shen WJ. Hormone-sensitive lipase: control of intracellular tri-(di-)acylglycerol and cholesteryl ester hydrolysis. J Lipid Res. 2002;43:1585–1594. - PubMed
-
- Osterlund T. Structure-function relationships of hormone-sensitive lipase. Eur J Biochem. 2001;268:1899–1907. - PubMed
-
- Shakur Y, Holst LS, Landstrom TR, Movsesian M, Degerman E, Manganiello V. Regulation and function of the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3) gene family. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;66:241–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
