miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature
- PMID: 16381832
- PMCID: PMC1347474
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkj112
miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature
Abstract
The miRBase database aims to provide integrated interfaces to comprehensive microRNA sequence data, annotation and predicted gene targets. miRBase takes over functionality from the microRNA Registry and fulfils three main roles: the miRBase Registry acts as an independent arbiter of microRNA gene nomenclature, assigning names prior to publication of novel miRNA sequences. miRBase Sequences is the primary online repository for miRNA sequence data and annotation. miRBase Targets is a comprehensive new database of predicted miRNA target genes. miRBase is available at http://microrna.sanger.ac.uk/.
Figures
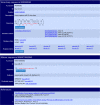
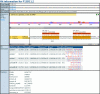
References
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Filipowicz W., Jaskiewicz L., Kolb F.A., Pillai R.S. Post-transcriptional gene silencing by siRNAs and miRNAs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2005;15:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Sontheimer E.J., Carthew R.W. Silence from within: endogenous siRNAs and miRNAs. Cell. 2005;122:9–12. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Kidner C.A., Martienssen R.A. The developmental role of microRNA in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005;8:38–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

