Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (www.nursa.org): hyperlinking the nuclear receptor signaling community
- PMID: 16381851
- PMCID: PMC1347392
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkj029
Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (www.nursa.org): hyperlinking the nuclear receptor signaling community
Abstract
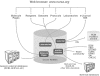
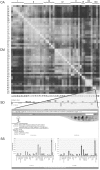
The nuclear receptor signaling (NRS) field has generated a substantial body of information on nuclear receptors, their ligands and coregulators, with the ultimate goal of constructing coherent models of the biological and clinical significance of these molecules. As a component of the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas (NURSA)--the development of a functional atlas of nuclear receptor biology--the NURSA Bioinformatics Resource is developing a strategy to organize and integrate legacy and future information on these molecules in a single web-based resource (www.nursa.org). This entails parallel efforts of (i) developing an appropriate software framework for handling datasets from NURSA laboratories and (ii) designing strategies for the curation and presentation of public data relevant to NRS. To illustrate our approach, we have described here in detail the development of a web-based interface for the NURSA quantitative PCR nuclear receptor expression dataset, incorporating bioinformatics analysis which provides novel perspectives on functional relationships between these molecules. We anticipate that the free and open access of the community to a platform for data mining and hypothesis generation strategies will be a significant contribution to the progress of research in this field.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas: catalyzing understanding of thyroid hormone signaling and metabolic control.Thyroid. 2008 Feb;18(2):113-22. doi: 10.1089/thy.2007.0247. Thyroid. 2008. PMID: 18279012
-
Minireview: Evolution of NURSA, the Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jun;23(6):740-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2009-0135. Epub 2009 May 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19423650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas: Opening Access to the Biology of Nuclear Receptor Signaling Pathways.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 1;10(9):e0135615. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135615. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26325041 Free PMC article.
-
The Nuclear Receptor Signaling Atlas: development of a functional atlas of nuclear receptors.Mol Endocrinol. 2005 Oct;19(10):2433-6. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0461. Epub 2005 Jul 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2005. PMID: 16051673
-
Nuclear receptors and bone.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007 Nov;1116:327-34. doi: 10.1196/annals.1402.043. Epub 2007 Sep 13. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007. PMID: 17872399 Review.
Cited by
-
A resource for integrated genomic analysis of the human liver.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 7;12(1):15151. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18506-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36071064 Free PMC article.
-
Luminal lncRNAs Regulation by ERα-Controlled Enhancers in a Ligand-Independent Manner in Breast Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 16;19(2):593. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020593. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29462945 Free PMC article.
-
ONRLDB--manually curated database of experimentally validated ligands for orphan nuclear receptors: insights into new drug discovery.Database (Oxford). 2015 Dec 4;2015:bav112. doi: 10.1093/database/bav112. Print 2015. Database (Oxford). 2015. PMID: 26637529 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptors in cancer - uncovering new and evolving roles through genomic analysis.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Mar;19(3):160-174. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.102. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29279606 Review.
-
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) gene deficiency impairs urine concentration in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Feb 11;111(6):2277-82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323977111. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24464484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tsai M.J., O'Malley B.W. Molecular mechanisms of action of steroid/thyroid receptor superfamily members. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld M.G., Glass C.K. Coregulator codes of transcriptional regulation by nuclear receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:36865–36868. - PubMed
-
- McKenna N.J., Lanz R.B., O'Malley B.W. Nuclear receptor coregulators: cellular and molecular biology. Endocr. Rev. 1999;20:321–344. - PubMed
-
- Margolis R.N., Evans R.M., O'Malley B.W. The nuclear receptor signaling atlas: development of a functional atlas of nuclear receptors. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005;19:2433–2436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

