RalB mobilizes the exocyst to drive cell migration
- PMID: 16382162
- PMCID: PMC1346891
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.26.2.727-734.2006
RalB mobilizes the exocyst to drive cell migration
Abstract
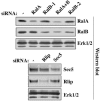
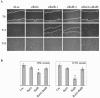
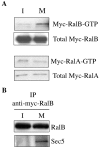
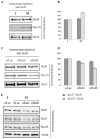
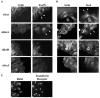
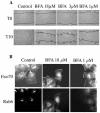
The Ras family GTPases RalA and RalB have been defined as central components of the regulatory machinery supporting tumor initiation and progression. Although it is known that Ral proteins mediate oncogenic Ras signaling and physically and functionally interact with vesicle trafficking machinery, their mechanistic contribution to oncogenic transformation is unknown. Here, we have directly evaluated the relative contribution of Ral proteins and Ral effector pathways to cell motility and directional migration. Through loss-of-function analysis, we find that RalA is not limiting for cell migration in normal mammalian epithelial cells. In contrast, RalB and the Sec6/8 complex or exocyst, an immediate downstream Ral effector complex, are required for vectorial cell motility. RalB expression is required for promoting both exocyst assembly and localization to the leading edge of moving cells. We propose that RalB regulation of exocyst function is required for the coordinated delivery of secretory vesicles to the sites of dynamic plasma membrane expansion that specify directional movement.
Figures

References
-
- Bhattacharya, M., P. H. Anborgh, A. V. Babwah, L. B. Dale, T. Dobransky, J. L. Benovic, R. D. Feldman, J. M. Verdi, R. J. Rylett, and S. S. Ferguson. 2002. Beta-arrestins regulate a Ral-GDS Ral effector pathway that mediates cytoskeletal reorganization. Nat. Cell Biol. 4:547-555. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher, M. S., and C. Aguado-Velasco. 1998. Membrane traffic during cell locomotion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10:537-541. - PubMed
-
- Brymora, A., V. A. Valova, M. R. Larsen, B. D. Roufogalis, and P. J. Robinson. 2001. The brain exocyst complex interacts with RalA in a GTP-dependent manner: identification of a novel mammalian Sec3 gene and a second Sec15 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 276:29792-29797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
