Pannus resolution after occipitocervical fusion in a non-rheumatoid atlanto-axial instability
- PMID: 16382308
- PMCID: PMC3489286
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-005-0969-4
Pannus resolution after occipitocervical fusion in a non-rheumatoid atlanto-axial instability
Abstract
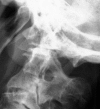
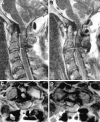
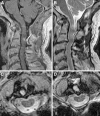
Periodontoid pseudotumor or pannus is considered to be an inflammatory mass most frequently associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Transoral resection of the pannus has been the treatment of choice for patients with associated myelopathy, followed in many instances by posterior stabilization. However, some authors have reported resolution of pannus associated with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of chronic atlanto-axial instability only after posterior stabilization. We report a case of a 69-year-old man who presented with a rapidly progressing myelopathy due to a retro-odontoid mass produced by chronic atlanto-axial instability associated with an occipital assimilation of C1 and tight posterior fossa. An urgent posterior fossa craniectomy followed by occipitocervical fixation was performed. After surgery, the patient's clinical condition improved and 1 year after surgery was asymptomatic, walked without any help and had normal strength. Control MR showed complete resolution of the retro-odontoid pannus.
Figures


References
-
- Crockard HA, Pozo JL, Ransford AO, Stevens JM, Kendall BE, Essigman WK. Transoral decompression and posterior fusion for rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68:350–356. - PubMed
-
- Joly-Torta MC, Martín-Ferrer S, Rimbau-Muñoz J, Domínguez C. Reducción de las masas periodontoideas tras artrodesis posterior: revisión a propósito de 2 casos no vinculados a artritis reumatoide. Neurocirugía (Astur) 2004;15:553–564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

