Nanoscale characterization and determination of adhesion forces of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili by using atomic force microscopy
- PMID: 16385026
- PMCID: PMC1347306
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.188.2.370-377.2006
Nanoscale characterization and determination of adhesion forces of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pili by using atomic force microscopy
Abstract
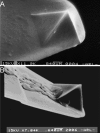
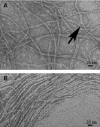
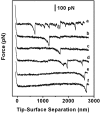
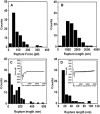
Type IV pili play an important role in bacterial adhesion, motility, and biofilm formation. Here we present high-resolution atomic force microscopy (AFM) images of type IV pili from Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteria. An individual pilus ranges in length from 0.5 to 7 microm and has a diameter from 4 to 6 nm, although often, pili bundles in which the individual filaments differed in both length and diameter were seen. By attaching bacteria to AFM tips, it was possible to fasten the bacteria to mica surfaces by pili tethers. Force spectra of tethered pili gave rupture forces of 95 pN. The slopes of force curves close to the rupture force were nearly linear but showed little variation with pilus length. Furthermore, force curves could not be fitted with wormlike-chain polymer stretch models when using realistic persistence lengths for pili. The observation that the slopes near rupture did not depend on the pili length suggests that they do not represent elastic properties of the pili. It is possible that this region of the force curves is determined by an elastic element that is part of the bacterial wall, although further experiments are needed to confirm this.
Figures




References
-
- Bieber, D., S. W. Ramer, C. Y. Wu, W. J. Murray, T. Tobe, R. Fernandez, and G. K. Schoolnik. 1998. Type IV pili, transient bacterial aggregates, and virulence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Science 280:2114-2118. - PubMed
-
- Boyd, J., T. Koga, and S. Lory. 1994. Identification and characterization of PilS, an essential regulator of pilin expression in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Gen. Genet. 243:565-574. - PubMed
-
- Craig, L., M. E. Pique, and J. A. Tainer. 2004. Type IV pilus structure and bacterial pathogenicity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:363-378. - PubMed
-
- Craig, L., R. K. Taylor, M. E. Pique, B. D. Adair, A. S. Arvai, M. Singh, S. J. Lloyed, D. S. Shin, E. D. Getzoff, M. Yeager, K. T. Forest, and J. A. Tainer. 2003. Type IV pilin structure and assembly: X-ray and EM analyses of Vibrio cholaere toxin-coregulated pilus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK pilin. Mol. Cell 11:1139-1150. - PubMed
-
- Dufrêne, Y. F. 2004. Using nanotechniques to explore microbial surfaces. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:451-460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

