AqpZ-mediated water permeability in Escherichia coli measured by stopped-flow spectroscopy
- PMID: 16385074
- PMCID: PMC1347286
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.188.2.820-822.2006
AqpZ-mediated water permeability in Escherichia coli measured by stopped-flow spectroscopy
Abstract
We report that the water permeability of wild-type Escherichia coli during exponential growth is comparable to that of an aqpZ disruption mutant. In contrast, an increase in permeability is observed for the wild type at the onset of the stationary stage with no significant corresponding change in the permeability of the mutant.
Figures
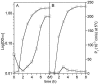
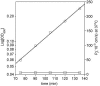
References
-
- Alemohammad, M. M., and C. J. Knowles. 1974. Osmotically induced volume and turbidity changes of Escherichia coli due to salts, sucrose, and glycerol, with particular reference to the rapid permeation of glycerol into the cell. J. Gen. Microbiol. 82(Part 1):125-142. - PubMed
-
- Borgnia, M. J., D. Kozono, G. Calamita, P. C. Maloney, and P. Agre. 1999. Functional reconstitution and characterization of AqpZ, the E. coli water channel protein. J. Mol. Biol. 291:1169-1179. - PubMed
-
- Bremer, E., and R. Kramer. 2000. Coping with osmotic challenges: osmoregulation through accumulation and release of compatible solutes in bacteria, p. 79-97. In G. Storz and R. Henggre-Aronis (ed.), Bacterial stress responses. ASM Press, Washington, D.C.
-
- Calamita, G., W. R. Bishai, G. M. Preston, W. B. Guggino, and P. Agre. 1995. Molecular cloning and characterization of AqpZ, a water channel from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 270:29063-29066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

