Mutations in a novel isoform of TRIOBP that encodes a filamentous-actin binding protein are responsible for DFNB28 recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss
- PMID: 16385458
- PMCID: PMC1380212
- DOI: 10.1086/499495
Mutations in a novel isoform of TRIOBP that encodes a filamentous-actin binding protein are responsible for DFNB28 recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss
Abstract
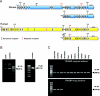
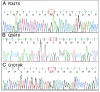
In a large consanguineous Palestinian kindred, we previously mapped DFNB28--a locus associated with recessively inherited, prelingual, profound sensorineural hearing impairment--to chromosome 22q13.1. We report here that mutations in a novel 218-kDa isoform of TRIOBP (TRIO and filamentous actin [F-actin] binding protein) are associated with DFNB28 hearing loss in a total of nine Palestinian families. Two nonsense mutations (R347X and Q581X) truncate the protein, and a potentially deleterious missense mutation (G1019R) occurs in a conserved motif in a putative SH3-binding domain. In seven families, 27 deaf individuals are homozygous for one of the nonsense mutations; in two other families, 3 deaf individuals are compound heterozygous for the two nonsense mutations or for Q581X and G1019R. The novel long isoform of TRIOBP has a restricted expression profile, including cochlea, retina, and fetal brain, whereas the original short isoform is widely expressed. Antibodies to TRIOBP reveal expression in sensory cells of the inner ear and colocalization with F-actin along the length of the stereocilia.
Figures




References
Web Resources
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for mouse long isoform of TRIOBP [accession number DQ278602], human long isoform of TRIOBP [accession number DQ278603], and transcripts from brain [accession number AB051449] and fetal brain [accession number AK096634])
-
- Hereditary Hearing Loss Homepage, http://webhost.ua.ac.be/hhh/
-
- UCSC Genome Browser, http://genome.ucsc.edu/
References
-
- Baldwin CT, Weiss S, Farrer LA, De Stefano AL, Adair R, Franklyn B, Kidd KK, Korostishevsky M, Bonne-Tamir B (1995) Linkage of congenital, recessive deafness (DFNB4) to chromosome 7q31 and evidence for genetic heterogeneity in the Middle Eastern Druze population. Hum Mol Genet 4:1637–1642 - PubMed
-
- Campbell DA, McHale DP, Brown KA, Moynihan LM, Houseman M, Karbani G, Parry G, Janjua AH, Newton V, al-Gazali L, Markham AF, Lench NJ, Mueller RF (1997) A new locus for non-syndromal, autosomal recessive, sensorineural hearing loss (DFNB16) maps to human chromosome 15q21-q22. J Med Genet 34:1015–1017 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

