Torsion of the gallbladder: report of a case
- PMID: 16385666
- PMCID: PMC2810604
- DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2005.46.6.862
Torsion of the gallbladder: report of a case
Abstract
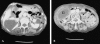
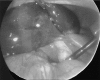
Torsion of the gallbladder is a rare entity that is difficult to diagnose preoperatively. The condition occurs most often in the elderly. Although its etiology is unknown, a constant finding is the presence of the gallbladder on a mobile mesentery (floating gallbladder). Torsion, or volvulus, of the gallbladder occurs when it twists axially, with the subsequent occlusion of bile and/or blood flow. Herein, a case of torsion of the gallbladder is presented where preoperative computed tomographic scan and laparoscopy were successfully used to diagnose and treat this condition without the usual requirement of open exploration. Given the possibility of laparoscopic cholecystectomy and the increasing incidence with which torsion of the gallbladder is being witnessed today, the importance of a preoperative computed tomographic scan is emphasized when there is a high index of clinical suspicion.
Figures
References
-
- Schroder DM, Cusumano DA., 3rd Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for gallbladder torsion. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1995;5:330–334. - PubMed
-
- Vosswinkel JA, Colantonio AL. Torsion of the gallbladder: laparoscopic identification and treatment. Surg Endosc. 1999;13:1154–1156. - PubMed
-
- Losken A, Wilson BW, Sherman R. Torsion of the gallbladder: a case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1997;63:975–978. - PubMed
-
- Kalimi R, Zarcone J, 3rd, McNelis J. Acute necrotizing torsion of the gallbladder. Am Surg. 2001;67:748–751. - PubMed
-
- Nakao A, Matsuda T, Funabiki S, Mori T, Koguchi K, Iwado T, et al. Gallbladder torsion: case report and review of 245 cases reported in the Japanese literature. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999;6:418–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

