Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of Eimeria infections in first-year grazing cattle
- PMID: 16387444
- PMCID: PMC7115786
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.11.022
Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of Eimeria infections in first-year grazing cattle
Abstract
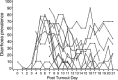
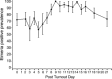
Infections with Eimeria parasites can lead to severe diarrhoea with considerable clinical and economic consequences in first-year grazing stock. To identify and characterise the cause of diarrhoea observed during previous years, 164 animals on 14 dairy farms in northwestern Germany were included in this study. The calves were physically and parasitologically examined prior to turnout and until 21 days post turnout (d.p.t.). Mean animal weights decreased from 194.9 kg at the start to 189.3 kg bodyweight at the end of the study. In all herds, oocyst counts were very low prior to turnout and increased after the calves had been kept on pasture for at least 7 days. On Day 9 post turnout, 90% and at the end of the study (21 d.p.t.) 70% of all animals showed Eimeria-positive faecal samples. During the course of the study, 79 (48.2%) animals passed faecal samples with more than 100,000 oocysts per gram. The predominant species identified was Eimeria alabamensis, which accounted for more than 83% of the oocysts counted. These parasitological findings matched the clinical observations. Diarrhoea was found in 130 (79.3%) of the study animals. At 5d.p.t. and thus prior to the rise of faecal oocyst counts, a significant increase in diarrhoea was recorded. Calves showing diarrhoea excreted statistically significantly more often over 100,000 E. alabamensis oocysts per gram faeces (0.28; p = 0.0002) than calves without diarrhoea. Diarrhoea was also found during significantly more study days in animals with high oocyst counts (0.39; p = 0.0001). These data indicate that in endemic areas first-year grazing calves must be considered at risk to develop clinical coccidiosis due to E. alabamensis infection during the first 2-3 weeks post turnout.
Figures




References
-
- Daugschies A., Akimura M., Burger H.-J. Experimental Eimeria bovis infections in the calf: 1. Parasitological and clinical findings. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1986;93:393–397. - PubMed
-
- Eckert, J., Taylor, M., Catchpole, J., Licois, D., Coudert, P., Bucklar, H., 1995. Morphological characteristics of oocysts, in: European Cooperation in the field of Scientific and Technical Research (COST). European Commission, Luxembourg, Report 89/820: Biotechnology—Guidelines on techniques in coccidiosis research, pp. 103–119.
-
- Emanuel C., Bianchi C., Biolatti B. Efficacy of toltrazuril in bovine coccidiosis. Vet. Med. Rev. 1988;59:90–91.
-
- Faber J.E., Kollmann D., Heise A., Bauer C., Failing K., Buerger H.J., Zahner H. Eimeria infections in cows in the periparturient phase and their calves: oocyst excretion and levels of specific serum and colostrum antibodies. Vet. Parasitol. 2002;104:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Gräfner G. Zur derzeitigen Verbreitung Bedeutung und Bekämpfung der Weideparasitosen des Rindes in der DDR. Monatsh. Veterinaermed. 1989;44:435–437.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

