Identification of a nitroimidazo-oxazine-specific protein involved in PA-824 resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 16387854
- PMCID: PMC1326169
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508392103
Identification of a nitroimidazo-oxazine-specific protein involved in PA-824 resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
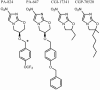
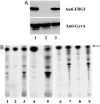
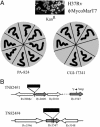
PA-824 is a promising new compound for the treatment of tuberculosis that is currently undergoing human trials. Like its progenitors metronidazole and CGI-17341, PA-824 is a prodrug of the nitroimidazole class, requiring bioreductive activation of an aromatic nitro group to exert an antitubercular effect. We have confirmed that resistance to PA-824 (a nitroimidazo-oxazine) and CGI-17341 (a nitroimidazo-oxazole) is most commonly mediated by loss of a specific glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (FGD1) or its deazaflavin cofactor F420, which together provide electrons for the reductive activation of this class of molecules. Although FGD1 and F420 are necessary for sensitivity to these compounds, they are not sufficient and require additional accessory proteins that directly interact with the nitroimidazole. To understand more proximal events in the reductive activation of PA-824, we examined mutants that were wild-type for both FGD1 and F420 and found that, although these mutants had acquired high-level resistance to PA-824 (and another nitroimidazo-oxazine), they retained sensitivity to CGI-17341 (and a related nitroimidazo-oxazole). Microarray-based comparative genome sequencing of these mutants identified lesions in Rv3547, a conserved hypothetical protein with no known function. Complementation with intact Rv3547 fully restored sensitivity to nitroimidazo-oxazines and restored the ability of Mtb to metabolize PA-824. These results suggest that the sensitivity of Mtb to PA-824 and related compounds is mediated by a protein that is highly specific for subtle structural variations in these bicyclic nitroimidazoles.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

