Pentapeptide repeat proteins
- PMID: 16388575
- PMCID: PMC2566302
- DOI: 10.1021/bi052130w
Pentapeptide repeat proteins
Abstract
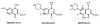
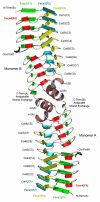
The pentapeptide repeat protein (PRP) family has more than 500 members in the prokaryotic and eukaryotic kingdoms. These proteins are composed of, or contain domains composed of, tandemly repeated amino acid sequences with a consensus sequence of [S,T,A,V][D,N][L,F][S,T,R][G]. The biochemical function of the vast majority of PRP family members is unknown. The three-dimensional structure of the first member of the PRP family was determined for the fluoroquinolone resistance protein (MfpA) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The structure revealed that the pentapeptide repeats encode the folding of a novel right-handed quadrilateral beta-helix. MfpA binds to DNA gyrase and inhibits its activity. The rod-shaped, dimeric protein exhibits remarkable similarity in size, shape, and electrostatics to DNA.
Figures





References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic Alignment Search Tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Kolter R, Moreno F. Genetics of Ribosomally Synthesized Peptide Antibiotics. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1992;46:141–163. - PubMed
-
- Krogh A, Brown M, Mian IS, Sjolander K, Haussler D. Hidden Markov Models in Computational Biology. J. Mol. Biol. 1994;235:1501–1531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

