Effects of cytochrome P450 3A modulators ketoconazole and carbamazepine on quetiapine pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 16390352
- PMCID: PMC1884989
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02507.x
Effects of cytochrome P450 3A modulators ketoconazole and carbamazepine on quetiapine pharmacokinetics
Abstract
Aims: To explore the potential for drug interactions on quetiapine pharmacokinetics using in vitro and in vivo assessments.
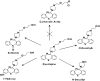
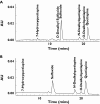
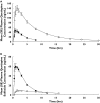
Methods: The CYP enzymes responsible for quetiapine metabolite formation were assessed using recombinant expressed CYPs and CYP-selective inhibitors. P-glycoprotein (Pgp) transport was tested in MDCK cells expressing the human MDR1 gene. The effects of CYP3A4 inhibition were evaluated clinically in 12 healthy volunteers that received 25 mg quetiapine before and after 4 days of treatment with ketoconazole 200 mg daily. To assess CYP3A4 induction in vivo, 18 patients with psychiatric disorders were titrated to steady-state quetiapine levels (300 mg twice daily), then titrated to 600 mg daily carbamazepine for 2 weeks.
Results: CYP3A4 was found to be responsible for formation of quetiapine sulfoxide and N- and O-desalkylquetiapine and not a Pgp substrate. In the clinical studies, ketoconazole increased mean quetiapine plasma C(max) by 3.35-fold, from 45 to 150 ng ml(-1) (mean C(max) ratio 90% CI 2.51, 4.47) and decreased its clearance (Cl/F) by 84%, from 138 to 22 l h(-1) (mean ratio 90% CI 0.13, 0.20). Carbamazepine decreased quetiapine plasma C(max) by 80%, from 1042 to 205 ng ml(-1) (mean C(max) ratio 90% CI 0.14, 0.28) and increased its clearance 7.5-fold, from 65 to 483 l h(-1) (mean ratio 90% CI 6.04, 9.28).
Conclusions: Cytochrome P450 3A4 is a primary enzyme responsible for the metabolic clearance of quetiapine. Quetiapine pharmacokinetics were affected by concomitant administration of ketoconazole and carbamazepine, and therefore other drugs and ingested natural products that strongly modulate the activity or expression of CYP3A4 would be predicted to change exposure to quetiapine.
Figures

References
-
- Markowitz JS, Brown CS, Moore TR. Atypical antipsychotics. Part I: pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy. Ann Pharmacother. 1999;33:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Goren JL, Levin GM. Quetiapine, an atypical antipsychotic. Pharmacotherapy. 1998;18:1183–94. - PubMed
-
- Seroquel (quetiapine fumarate, AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE). Full prescribing information, 2004.
-
- Prior TI, Chue PS, Tibbo P, Baker GB. Drug metabolism and atypical antipsychotics. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 1999;9:301–9. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka E, Hisawa S. Clinically significant pharmacokinetic drug interactions with psychoactive drugs: antidepressants and antipsychotics and the cytochrome P450 system. J Clin Pharm Ther. 1999;24:7–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

