A novel method of modifying immune responses by vaccination with lipiodol-siRNA mixtures
- PMID: 16390542
- PMCID: PMC1343589
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-4-2
A novel method of modifying immune responses by vaccination with lipiodol-siRNA mixtures
Abstract
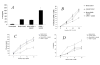
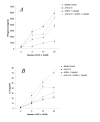
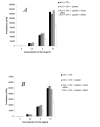
The dendritic cell (DC) possesses the ability to stimulate both T helper 1 (Th1) and Th2 responses depending on activation stimuli. Although it is known that chemically or genetically modified DC can be used therapeutically to steer immune responses towards either Th1 or Th2, cellular therapy with ex vivo manipulated DC is clinically difficult. Here we demonstrate a novel method of switching immune responses from Th1 to Th2 through in vivo immune modulation by administration of siRNA. We demonstrate that siRNA targeting of the IL-12p35 gene leads to a Th2 bias in vitro through an IL-10 dependent mechanism. In vivo administration of siRNA admixed with the oil-based contrast agent lipiodol in the presence of antigen and adjuvant induced a deviation in recall response to reduced production of IFN-gamma and augmented IL-4 response using either KLH or ovalbumin. This simple method of in vivo modification of immune response possesses therapeutic potential in Th1-mediated diseases such as multiple sclerosis and autoimmune diabetes.
Figures
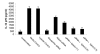

Similar articles
-
IL-12, as an adjuvant, promotes a T helper 1 cell, but does not suppress a T helper 2 cell recall response.J Immunol. 1996 Feb 1;156(3):887-94. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8558014
-
Limiting dilution analysis of CD4 T-cell cytokine production in mice administered native versus polymerized ovalbumin: directed induction of T-helper type-1-like activation.Immunology. 1996 Jan;87(1):119-26. Immunology. 1996. PMID: 8666423 Free PMC article.
-
The mast cell mediator PGD2 suppresses IL-12 release by dendritic cells leading to Th2 polarized immune responses in vivo.Immunobiology. 2006;211(6-8):463-72. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2006.05.020. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Immunobiology. 2006. PMID: 16920486
-
Effects of immunomodulators on the response induced by vaccines against autoimmune diseases.Autoimmunity. 2017 Nov;50(7):393-402. doi: 10.1080/08916934.2017.1373766. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Autoimmunity. 2017. PMID: 28906131 Review.
-
Induction of Interleukin-10 Producing Dendritic Cells As a Tool to Suppress Allergen-Specific T Helper 2 Responses.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00455. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616018 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of antitumor immunity through xenoplacental immunization.J Transl Med. 2006 May 25;4:22. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-4-22. J Transl Med. 2006. PMID: 16725035 Free PMC article.
-
RORC2 gene silencing in human Th17 cells by siRNA: design and evaluation of highly efficient siRNA.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2013 Jan;5(1):10-9. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23626872 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumoral effect of local injection of TLR-9 agonist emulsified in Lipiodol with systemic anti-PD-1 in a murine model of colorectal carcinoma.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 16;14:1272246. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272246. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38292484 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous ascorbic acid to prevent and treat cancer-associated sepsis?J Transl Med. 2011 Mar 4;9:25. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-25. J Transl Med. 2011. PMID: 21375761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone. I. Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol. 1986;136:2348–2357. - PubMed
-
- Singh VK, Mehrotra S, Agarwal SS. The paradigm of Th1 and Th2 cytokines: its relevance to autoimmunity and allergy. Immunol Res. 1999;20:147–161. - PubMed
-
- Sospedra M, Martin R. Immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004. - PubMed
-
- Miossec P, van den Berg W. Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:2105–2115. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

