Virological, serological, and clinical features of an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis due to recombinant genogroup II norovirus in an infant home
- PMID: 16390967
- PMCID: PMC1351937
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.44.1.177-182.2006
Virological, serological, and clinical features of an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis due to recombinant genogroup II norovirus in an infant home
Abstract
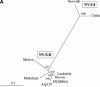
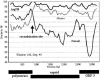
Norovirus (NV) is an important cause of acute nonbacterial gastroenteritis worldwide. Recently, several sporadic cases due to naturally occurring recombinant NVs have been reported. In January 2000, there was an outbreak of gastroenteritis in an infant home in Sapporo, Japan. Of 34 residents of the home that were less than 2 years old, 23 developed gastrointestinal symptoms and NV infection was confirmed by conventional reverse transcription-PCR to detect the RNA polymerase region of genogroup II NV. In this virus, the RNA polymerase region shared 86% nucleotide identity with Hawaii virus but only 77% with Mexico virus; however, its capsid region shared only 70% identity with Hawaii virus but 90% with Mexico virus. On the other hand, both regions shared a higher 96% nucleotide identity with Arg320 virus, which was found in Mendoza, Argentina, in 1995 and considered to be a recombinant of Hawaii and Mexico viruses. The findings indicate that the virus involved in the outbreak was similar and may have evolved from the Arg320 virus. Clinically the cases were more severe than those of previously reported sporadic or outbreak cases of NV infection.
Figures


References
-
- Ando, T., S. S. Monroe, J. S. Noel, and R. I. Glass. 1997. A one-tube method of reverse transcription-PCR to efficiently amplify a 3-kilobase region from the RNA polymerase gene to the poly(A) tail of small round-structured viruses (Norwalk-like viruses). J. Clin. Microbiol. 35:570-577. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ando, T., J. S. Noel, and R. L. Fankhauser. 2000. Genetic classification of “Norwalk-like viruses.” J. Infect. Dis. 181:S336-S348. - PubMed
-
- Belliot, G., H. Laveran, and S. S. Monroe. 1997. Detection and genetic differentiation of human astrovirus: phylogenetic grouping varies by coding region. Arch. Virol. 142:1323-1334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

