Improvement of alpha-amylase production by modulation of ribosomal component protein S12 in Bacillus subtilis 168
- PMID: 16391027
- PMCID: PMC1352260
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.71-77.2006
Improvement of alpha-amylase production by modulation of ribosomal component protein S12 in Bacillus subtilis 168
Abstract
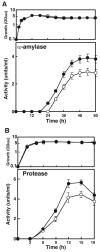
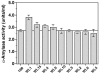
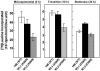
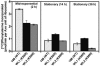
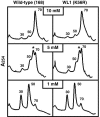
The capacity of ribosomal modification to improve antibiotic production by Streptomyces spp. has already been demonstrated. Here we show that introduction of mutations that produce streptomycin resistance (str) also enhances alpha-amylase (and protease) production by a strain of Bacillus subtilis as estimated by measuring the enzyme activity. The str mutations are point mutations within rpsL, the gene encoding the ribosomal protein S12. In vivo as well as in vitro poly(U)-directed cell-free translation systems showed that among the various rpsL mutations K56R (which corresponds to position 42 in E. coli) was particularly effective at enhancing alpha-amylase production. Cells harboring the K56R mutant ribosome exhibited enhanced translational activity during the stationary phase of cell growth. In addition, the K56R mutant ribosome exhibited increased 70S complex stability in the presence of low Mg2+ concentrations. We therefore conclude that the observed increase in protein synthesis activity by the K56R mutant ribosome reflects increased stability of the 70S complex and is responsible for the increase in alpha-amylase production seen in the affected strain.
Figures

References
-
- Bertoldo, C., and G. Antranikian. 2002. Starch-hydrolyzing enzymes from thermophilic archaea and bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 6:151-160. - PubMed
-
- Carter, A. P., W. M. Clemons, D. E. Brodersen, R. J. Morgan-Warren, B. T. Wimberly, and V. Ramakrishnan. 2000. Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature 407:340-348. - PubMed
-
- Cundliffe, E. 1990. Recognition sites for antibiotics within rRNA, p. 479-490. In A. D. W. E. Hill, R. A. Garrett, P. B. Moore, D. Schlessinger, and J. R. Warner (ed.), The ribosome: structure, function, and evolution. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D. C.
-
- Fujimoto, Z., K. Takase, N. Doui, M. Momma, T. Matsumoto, and H. Mizuno. 1998. Crystal structure of a catalytic-site mutant α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis complexed with maltopentaose. J. Mol. Biol. 277:393-407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

