Occurrence and genetic diversity of uncultured Legionella spp. in drinking water treated at temperatures below 15 degrees C
- PMID: 16391038
- PMCID: PMC1352175
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.157-166.2006
Occurrence and genetic diversity of uncultured Legionella spp. in drinking water treated at temperatures below 15 degrees C
Abstract
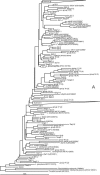
Representatives of the genus Legionella were detected by use of a real-time PCR method in all water samples collected directly after treatment from 16 surface water (SW) supplies prior to postdisinfection and from 81 groundwater (GW) supplies. Legionella concentrations ranged from 1.1 x 10(3) to 7.8 x 10(5) cells liter(-1) and were significantly higher in SW treated with multiple barriers at 4 degrees C than in GW treated at 9 to 12 degrees C with aeration and filtration but without chemical disinfection. No Legionellae (<50 CFU liter(-1)) were detected in treated water by the culture method. Legionella was also observed in untreated SW and in untreated aerobic and anaerobic GW. Filtration processes in SW and GW treatment had little effect or increased the Legionella concentration, but ozonation in SW treatment caused about 1-log-unit reduction. A phylogenetic analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences of 202 clones, obtained from a selection of samples, showed a high similarity (>91%) with Legionella sequences in the GenBank database. A total of 40 (33%) of the 16S rRNA gene sequences obtained from treated water were identified as described Legionella species and types, including L. bozemanii, L. worsleiensis, Legionella-like amoebal pathogen types, L. quateirensis, L. waltersii, and L. pneumophila. 16S rRNA gene sequences with a similarity of below 97% from described species were positioned all over the phylogenetic tree of Legionella. Hence, a large diversity of yet-uncultured Legionellae are common members of the microbial communities in SW and GW treated at water temperatures of below 15 degrees C.
Figures


References
-
- Adeleke, A. A., B. S. Fields, R. F. Benson, M. I. Daneshvar, J. M. Pruckler, R. M. Ratcliff, T. G. Harrison, R. S. Weyant, R. J. Birtles, D. Raoult, and M. A. Halablab. 2001. Legionella drozanskii sp. nov., Legionella rowbothamii sp. nov. and Legionella fallonii sp. nov.: three unusual new Legionella species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51:1151-1160. - PubMed
-
- Alary, M., and J. R. Joly. 1992. Comparison of culture methods and an immunofluorescence assay for the detection of Legionella pneumophila in domestic hot water devices. Curr. Microbiol. 25:19-23. - PubMed
-
- Althaus, H. 1987. Legionellas in drinking, bathing and warm water. Offentl. Gesundheitswes 49(Suppl. 1):8-13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

