Novel surface display system for proteins on non-genetically modified gram-positive bacteria
- PMID: 16391130
- PMCID: PMC1352190
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.880-889.2006
Novel surface display system for proteins on non-genetically modified gram-positive bacteria
Abstract
A novel display system is described that allows highly efficient immobilization of heterologous proteins on bacterial surfaces in applications for which the use of genetically modified bacteria is less desirable. This system is based on nonliving and non-genetically modified gram-positive bacterial cells, designated gram-positive enhancer matrix (GEM) particles, which are used as substrates to bind externally added heterologous proteins by means of a high-affinity binding domain. This binding domain, the protein anchor (PA), was derived from the Lactococcus lactis peptidoglycan hydrolase AcmA. GEM particles were typically prepared from the innocuous bacterium L. lactis, and various parameters for the optimal preparation of GEM particles and binding of PA fusion proteins were determined. The versatility and flexibility of the display and delivery technology were demonstrated by investigating enzyme immobilization and nasal vaccine applications.
Figures



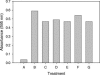
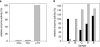

References
-
- Andreoni, C., L. Goetsch, C. Libon, P. Samuelson, T. N. Nguyen, A. Robert, M. Uhlen, H. Binz, and S. Stahl. 1997. Flow cytometric quantification of surface-displayed recombinant receptors on staphylococci. BioTechniques 23:696-702, 704. - PubMed
-
- Bateman, A., and M. Bycroft. 2000. The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD). J. Mol. Biol. 299:1113-1119. - PubMed
-
- Buist, G. 1997. AcmA of Lactococcus lactis, a cell-binding major autolysin. Ph.D. thesis. University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

