Naturally transformable Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 belongs to the newly described species Acinetobacter baylyi
- PMID: 16391138
- PMCID: PMC1352221
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.72.1.932-936.2006
Naturally transformable Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 belongs to the newly described species Acinetobacter baylyi
Abstract
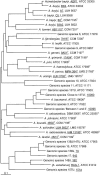
Genotypic and phenotypic analyses were carried out to clarify the taxonomic position of the naturally transformable Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1. Transfer tDNA-PCR fingerprinting, 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, and selective restriction fragment amplification (amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis) indicate that strain ADP1 and a second transformable strain, designated 93A2, are members of the newly described species Acinetobacter baylyi. Transformation assays demonstrate that the A. baylyi type strain B2(T) and two other originally identified members of the species (C5 and A7) also have the ability to undergo natural transformation at high frequencies, confirming that these five strains belong to a separate species of the genus Acinetobacter, characterized by the high transformability of its strains that have been cultured thus far.
Figures


References
-
- Barbe, V., D. Vallenet, N. Fonknechten, A. Kreimeyer, S. Oztas, L. Labarre, S. Cruveiller, C. Robert, S. Duprat, P. Wincker, L. N. Ornston, J. Weissenbach, P. Marliere, G. N. Cohen, and C. Medigue. 2004. Unique features revealed by the genome sequence of Acinetobacter sp. ADP1, a versatile and naturally transformation competent bacterium. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:5766-5779. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouvet, P. J., and P. A. Grimont. 1987. Identification and biotyping of clinical isolates of Acinetobacter. Ann. Inst. Pasteur Microbiol. 138:569-578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

