Imaging chemically modified adenovirus for targeting tumors expressing integrin alphavbeta3 in living mice with mutant herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase PET reporter gene
- PMID: 16391197
- PMCID: PMC4154793
Imaging chemically modified adenovirus for targeting tumors expressing integrin alphavbeta3 in living mice with mutant herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase PET reporter gene
Abstract
The aim of this study was to change adenovirus tropism by chemical modification of the fiber knobs with PEGylated RGD peptide for targeting integrin alpha(v)beta(3) that is uniquely or highly expressed in tumor cells and neovasculature of tumors of various origins.
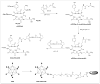
Methods: The first generation Ad (Ad) vector, which expresses the herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant thymidine kinase (HSV1-sr39tk) gene under the control of cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter was conjugated with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) or RGD-PEG. The transduction efficiency of Ads (Adtk, PEG-Adtk, and RGD-PEG-Adtk) into different types of cells (293T, MCF7, MDA-MB-435, and U87MG) was analyzed and quantified by thymidine kinase (TK) assay using 8-(3)H-penciclovir (8-(3)H-PCV) as substrate. The in vivo infectivity of the Ad vectors after intravenous administration into integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-positive U87MG and MDA-MB-435 tumor-bearing athymic nude mice was measured by both noninvasive microPET using 9-[4-(18)F-fluoro-3-(hydroxymethyl)butyl]guanine ((18)F-FHBG) as a reporter probe and ex vivo TK assay of the tumor and tissue homogenates.
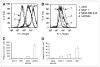
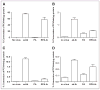
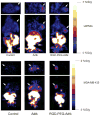
Results: PEGylation completely abrogated coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor (CAR)-knob interaction and the infectivity of PEG-Adtk is significantly lower than that of unmodified Adtk in CAR-positive cells. RGD-PEG-modified virus (RGD-PEG-Adtk) had significantly higher infectivity than PEG-Adtk and the extent of increase is related to both CAR and integrin alpha(v)beta(3) expression levels. (18)F-FHBG had minimal nonspecific uptake in the liver and tumors that are void of sr39tk. Mice preinjected intravenously with unmodified Adtk resulted in high hepatic uptake and moderate tumor accumulation of the tracer. In contrast, RGD-PEG-Adtk administration resulted in significantly lower liver uptake without compromising the tumor accumulation of (18)F-FHBG. Expression of TK in the liver and tumor homogenates corroborated with the magnitude of (18)F-FHBG uptake quantified by noninvasive microPET. Analysis of liver and tumor tissue integrin level confirmed that RGD-integrin interaction is responsible for the enhanced tumor infectivity of RGD-PEG-Adtk.
Conclusion: The results of this study suggest that RGD-PEG conjugation is an effective way to modify Ad vector tropism for improved systemic gene delivery. Noninvasive PET and (18)F-FHBG are able to monitor in vivo transfectivity of both Adtk and RGD-PEG-Adtk vectors in the liver and tumors after intravenous injection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PET of cardiac transgene expression: comparison of 2 approaches based on herpesviral thymidine kinase reporter gene.J Nucl Med. 2004 Nov;45(11):1917-23. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15534063
-
Pegylated Arg-Gly-Asp peptide: 64Cu labeling and PET imaging of brain tumor alphavbeta3-integrin expression.J Nucl Med. 2004 Oct;45(10):1776-83. J Nucl Med. 2004. PMID: 15471848
-
Comparison between adenoviral and retroviral vectors for the transduction of the thymidine kinase PET reporter gene in rat mesenchymal stem cells.J Nucl Med. 2008 Nov;49(11):1836-44. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.052175. J Nucl Med. 2008. PMID: 18984872
-
Ad5-(PSE-BC)-(GAL4-(VP16)2)-(GAL4)5-sr39tk.2008 Dec 15 [updated 2009 Jan 5]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2008 Dec 15 [updated 2009 Jan 5]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641191 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
9-(4-[18F]Fluoro-3-hydroxymethylbutyl)guanine.2005 Jan 24 [updated 2005 Feb 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2005 Jan 24 [updated 2005 Feb 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641753 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Retargeting adenoviral vectors to improve gene transfer into tumors.Cancer Gene Ther. 2011 Apr;18(4):275-87. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2010.78. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011. PMID: 21183946 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic opportunities of small interfering RNA.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;23(4):367-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2009.00694.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19709318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantitative PET of EGFR expression in xenograft-bearing mice using 64Cu-labeled cetuximab, a chimeric anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007 Jun;34(6):850-8. doi: 10.1007/s00259-006-0361-6. Epub 2007 Jan 30. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17262214
-
Targeted delivery of siRNA.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006;2006(4):63675. doi: 10.1155/JBB/2006/63675. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17057365 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Gene Delivery: Strategies to Engineer the Surfaces of Viral Vectors.Biomedicines. 2013 Dec 4;1(1):3-16. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines1010003. Biomedicines. 2013. PMID: 28548054 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith AE. Viral vectors in gene therapy. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1995;49:807–838. - PubMed
-
- Kanerva A, Hemminki A. Modified adenovirus for cancer gene therapy. Int J Cancer. 2004;110:475–480. - PubMed
-
- Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, et al. Isolation of a common receptor for coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science. 1997;275:1320–1323. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
